Transcription-dependent R-loop formation at mammalian class switch sequences
- PMID: 10698946
- PMCID: PMC305644
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.5.1055
Transcription-dependent R-loop formation at mammalian class switch sequences
Retraction in
-
Transcription-dependent R-loop formation at mammalian class switch sequences.EMBO J. 2001 Sep 1;19(17):4855. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdd511. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 12134869 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
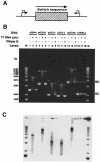
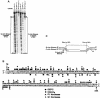
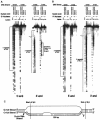
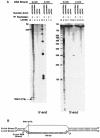
Immunoglobulin class switching is mediated by recombination between switch sequences located immediately upstream of the immunoglobulin constant heavy chain genes. Targeting of recombination to particular switch sequences is associated temporally with transcription through these regions. We recently have provided evidence for inducible and stable RNA-DNA hybrid formation at switch sequences in the mouse genome that are mechanistically important for class switching in vivo. Here, we define in vitro the precise configuration of the DNA and RNA strands within this hybrid structure at the Smicro, Sgamma3 and Sgamma2b mouse switch sequences. We find that the G-rich (non-template) DNA strand of each switch sequence is hypersensitive to probes throughout much of its length, while the C-rich (template) DNA strand is essentially resistant. These results demonstrate formation of an R-loop, whereby the G-rich RNA strand forms a stable heteroduplex with its C-rich DNA strand counterpart, and the G-rich DNA strand exists primarily in a single-stranded state. We propose that the organized structure of the R-loop is essential for targeting the class switch recombination machinery to these sequences.
Figures

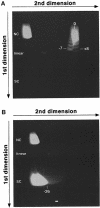
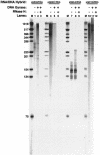
Comment in
-
Findings of scientific misconduct.NIH Guide Grants Contracts (Bethesda). 2002 May 30:NOT-OD-02-051. NIH Guide Grants Contracts (Bethesda). 2002. PMID: 12449911 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baker T.A. and Kornberg, A. (1988) Transcriptional activation of initiation of replication from the E.coli chromosomal origin: an RNA–DNA hybrid near oriC. Cell, 55, 113–123. - PubMed
-
- Carles-Kinch K. and Kreuzer, K.N. (1997) RNA–DNA hybrid formation at a bacteriophage T4 replication origin. J. Mol. Biol., 266, 915–926. - PubMed
-
- Champoux J.J. and McConaughy, B.L. (1975) Priming of superhelical SV40 DNA by E.coli RNA polymerase for in vitro DNA synthesis. Biochemistry, 14, 307–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

