Functional interaction between RAFT1/FRAP/mTOR and protein kinase cdelta in the regulation of cap-dependent initiation of translation
- PMID: 10698949
- PMCID: PMC305647
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.5.1087
Functional interaction between RAFT1/FRAP/mTOR and protein kinase cdelta in the regulation of cap-dependent initiation of translation
Abstract
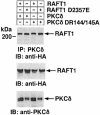
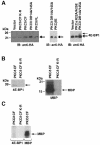
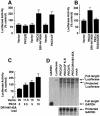
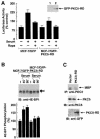
Hormones and growth factors induce protein translation in part by phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) binding protein 1 (4E-BP1). The rapamycin and FK506-binding protein (FKBP)-target 1 (RAFT1, also known as FRAP) is a mammalian homolog of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae target of rapamycin proteins (mTOR) that regulates 4E-BP1. However, the molecular mechanisms involved in growth factor-initiated phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 are not well understood. Here we demonstrate that protein kinase Cdelta (PKCdelta) associates with RAFT1 and that PKCdelta is required for the phosphorylation and inactivation of 4E-BP1. PKCdelta-mediated phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 is wortmannin resistant but rapamycin sensitive. As shown for serum, phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 by PKCdelta inhibits the interaction between 4E-BP1 and eIF4E and stimulates cap-dependent translation. Moreover, a dominant-negative mutant of PKCdelta inhibits serum-induced phosphorylation of 4E-BP1. These findings demonstrate that PKCdelta associates with RAFT1 and thereby regulates phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and cap-dependent initiation of protein translation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Feb 17;95(4):1432-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.4.1432. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9465032 Free PMC article.
-
4E-BP1, a repressor of mRNA translation, is phosphorylated and inactivated by the Akt(PKB) signaling pathway.Genes Dev. 1998 Feb 15;12(4):502-13. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.4.502. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9472019 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the rapamycin and FKBP-target 1/mammalian target of rapamycin and cap-dependent initiation of translation by the c-Abl protein-tyrosine kinase.J Biol Chem. 2000 Apr 14;275(15):10779-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.15.10779. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10753870
-
4E-BP1, a multifactor regulated multifunctional protein.Cell Cycle. 2016;15(6):781-6. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1151581. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 26901143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mTOR/4E-BP1/eIF4E Signalling Pathway as a Source of Cancer Drug Targets.Curr Med Chem. 2022;29(20):3501-3529. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220224112042. Curr Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35209811 Review.
Cited by
-
The cationic amino acid transporters CAT1 and CAT3 mediate NMDA receptor activation-dependent changes in elaboration of neuronal processes via the mammalian target of rapamycin mTOR pathway.J Neurosci. 2007 Jan 17;27(3):449-58. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4489-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17234578 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic adaptation of skeletal muscle to hyperammonemia drives the beneficial effects of l-leucine in cirrhosis.J Hepatol. 2016 Nov;65(5):929-937. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.06.004. Epub 2016 Jun 16. J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27318325 Free PMC article.
-
Ca(2+)-independent protein kinase C activity is required for alpha1-adrenergic-receptor-mediated regulation of ribosomal protein S6 kinases in adult cardiomyocytes.Biochem J. 2003 Jul 15;373(Pt 2):603-11. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030454. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12720544 Free PMC article.
-
AICAR treatment for 14 days normalizes obesity-induced dysregulation of TORC1 signaling and translational capacity in fasted skeletal muscle.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Dec;299(6):R1546-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00337.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20844264 Free PMC article.
-
Translational up-regulation and high-level protein expression from plasmid vectors by mTOR activation via different pathways in PC3 and 293T cells.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 28;5(12):e14408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014408. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21203441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham R.T. (1996) Phosphoinositol 3-kinase related kinases. Curr. Opin. Immunol., 8, 412–418. - PubMed
-
- Alessi D.R., et al. (1997) Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1): structural and functional homology with the Drosophila DSTPK61 kinase. Curr. Biol., 7, 776–789. - PubMed
-
- Belham C., Wu, S. and Avruch, J. (1999) Intracellular signaling: PDK1–a kinase at the hub of things. Curr. Biol., 9, R93–R96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

