Comparison of a new neuraminidase detection assay with an enzyme immunoassay, immunofluorescence, and culture for rapid detection of influenza A and B viruses in nasal wash specimens
- PMID: 10699013
- PMCID: PMC86363
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.3.1161-1165.2000
Comparison of a new neuraminidase detection assay with an enzyme immunoassay, immunofluorescence, and culture for rapid detection of influenza A and B viruses in nasal wash specimens
Abstract
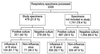
The performance of a new, rapid, easy-to-perform assay based on neuraminidase enzyme activity for detection of influenza virus types A and B was compared to detection by culture, indirect immunofluorescence, and enzyme immunoassay in 479 nasal wash specimens from children with respiratory infections. Compared to isolation of influenza virus by culture, the neuraminidase assay had a sensitivity of 70.1%, specificity of 92.4%, positive predictive value of 76.3%, and negative predictive value of 89.9%. There was a higher sensitivity for the detection of influenza A virus (76.4%) than for influenza B virus (40.9%). Indirect immunofluorescence showed a sensitivity of 59.8% and specificity of 97% compared to culture isolation for detection of influenza A and B viruses. Enzyme immunoassay showed a sensitivity of 89.7% and specificity of 98.1% for the detection of influenza A alone. The quality of the nasal wash specimen had a significant effect on the detection of influenza virus by all of the assays. A strong response of the neuraminidase assay was more likely to represent a culture-confirmed influenza infection. This new rapid neuraminidase assay was useful for the detection of influenza A and B viruses in nasal wash specimens.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of lateral-flow immunoassay and enzyme immunoassay with viral culture for rapid detection of influenza virus in nasal wash specimens from children.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 May;41(5):2132-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.5.2132-2134.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12734259 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a neuraminidase detection assay for the rapid detection of influenza A and B virus in children.Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2000 Mar-Apr;3(2):162-7. doi: 10.1007/s100240050020. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10679035 Clinical Trial.
-
[The rapid detection kit based on neuraminidase activity of influenza virus].Nihon Rinsho. 2000 Nov;58(11):2234-7. Nihon Rinsho. 2000. PMID: 11225310 Review. Japanese.
-
Evaluation of BioStar FLU OIA assay for rapid detection of influenza A and B viruses in respiratory specimens.J Clin Virol. 2000 Aug;17(2):119-26. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(00)00081-0. J Clin Virol. 2000. PMID: 10942092
-
Simultaneous detection and typing of influenza viruses A and B by a nested reverse transcription-PCR: comparison to virus isolation and antigen detection by immunofluorescence and optical immunoassay (FLU OIA).J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Jan;39(1):134-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.1.134-138.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11136761 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Use of induced sputum for the diagnosis of influenza and infections in asthma: a comparison of diagnostic techniques.J Clin Virol. 2003 Apr;26(3):339-46. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(02)00084-7. J Clin Virol. 2003. PMID: 12637083 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of lateral-flow immunoassay and enzyme immunoassay with viral culture for rapid detection of influenza virus in nasal wash specimens from children.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 May;41(5):2132-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.5.2132-2134.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12734259 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of a new lateral-flow chromatographic membrane immunoassay to viral culture for rapid detection and differentiation of influenza A and B viruses in respiratory specimens.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Aug;42(8):3661-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3661-3664.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15297513 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical evaluation of the ZstatFlu-II test: a chemiluminescent rapid diagnostic test for influenza virus.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Jul;40(7):2331-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.7.2331-2334.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12089243 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a new dot blot enzyme immunoassay (directigen flu A+B) for simultaneous and differential detection of influenza a and B virus antigens from respiratory samples.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Sep;40(9):3515-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.9.3515-3517.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12202608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atmar R L, Baxter B D. Typing and subtyping clinical isolates of influenza virus using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Clin Diagn Virol. 1996;7:77–84. - PubMed
-
- Correa A G, Allen C, Taber L H, Couch R B. Program and abstracts of the 32nd Infectious Diseases Society of America Annual Meeting. Washington, D.C.: Infectious Diseases Society of America; 1994. Comparison of clinical specimens in the rapid diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants, abstr. 327; p. 56A.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical