Detection of a previously unamplified spacer within the DR locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: epidemiological implications
- PMID: 10699028
- PMCID: PMC86384
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.3.1231-1234.2000
Detection of a previously unamplified spacer within the DR locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: epidemiological implications
Abstract
Spoligotyping, a method based on the variability of distribution of the 43 inter-direct repeat (DR) spacers of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis BCG, is useful to study the molecular epidemiology of bovine and human tuberculosis. Recently, a major family of M. tuberculosis clinical isolates named the Haarlem family, which did not contain spacers 31 and 33 to 36, was reported in a multicenter study. Independently, a data bank containing all the published spoligotypes showed that the two most prevalent spoligotypes in the world differed only by the presence or absence of spacer 31. A careful analysis of the DR locus sequence led us to hypothesize that spacer 31 may not have been amplified in some isolates with the primer sets DRa and DRb currently used for spoligotyping. Consequently, a modified spoligotyping method based on different combinations of the 36-bp DR and IS6110 primers was devised that was able to discriminate between the left and the right parts of the DR locus and demonstrated the presence of the previously unamplified spacer 31 for some of the clinical isolates. By analogy, we suggest that a single-spacer difference in some epidemiologically linked cases of tuberculosis may simply arise due to the insertion of an extra copy of IS6110 within the DR locus, leading to its asymmetrical disruption and subsequent lack of the DRa or DRb targets. The influence of the IS6110 preferential insertion sites within the DR locus on spoligotyping results should be further investigated.
Figures
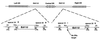


References
-
- Alito A, Morcillo N, Scipioni S, Dolmann A, Romano M I, Cataldi A, van Soolingen D. The IS6110 restriction fragment length polymorphism in particular multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains may evolve too fast for reliable use in outbreak investigation. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:788–791. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bifani P J, Plikaytis B B, Kapur V, Stockbauer K, Pan X, Lutfey M L, Moghazeh S L, Eisner W, Daniel T M, Kaplan M H, Musser J M, Kreiswirth B N. Origin and interstate spread of a New York City multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clone family. JAMA. 1996;275:452–457. - PubMed
-
- De Boer A S, Borgdoff M W, de Haas P E, Nagelkerke N J, van Embden J D A, van Soolingen D. Analysis of rate of change of IS6110 RFLP patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on serial patient isolates. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:1238–1244. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

