Molecular characterization of Brucella strains isolated from marine mammals
- PMID: 10699036
- PMCID: PMC86392
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.3.1258-1262.2000
Molecular characterization of Brucella strains isolated from marine mammals
Abstract
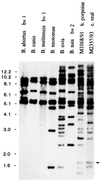
Recently, gram-negative bacteria isolated from a variety of marine mammals have been identified as Brucella species by conventional phenotypic analysis. This study found the 16S rRNA gene from one representative isolate was identical to the homologous sequences of Brucella abortus, B. melitensis, B. canis, and B. suis. IS711-based DNA fingerprinting of 23 isolates from marine mammals showed all the isolates differed from the classical Brucella species. In general, fingerprint patterns grouped by host species. The data suggest that the marine mammal isolates are distinct types of Brucella and not one of the classical species or biovars invading new host species. In keeping with historical precedent, the designation of several new Brucella species may be appropriate.
Figures


References
-
- Alton G G, Jones L M, Pietz D E. Monograph series. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1975. Laboratory techniques in brucellosis. - PubMed
-
- Clavareau C, Wellemans V, Walravens K, Tryland M, Verger M J, Grayson M, Cloeckaert A, Letesson J J, Godfroid J. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of a Brucella strain isolated from a minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata) Microbiology. 1998;144:3267–3273. - PubMed
-
- Corbel M J. International committee on systematic bacteriology—subcommittee on the taxonomy of Brucella. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1988;38:450–452.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

