Increased expression of CD40 ligand (CD154) on CD4+ T cells as a marker of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 10700427
- PMCID: PMC1753086
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.59.3.190
Increased expression of CD40 ligand (CD154) on CD4+ T cells as a marker of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: The interaction between the activation induced surface glycoprotein CD40L (ligand) (CD154) on CD4+ T cells and its receptor CD40, which is expressed on various cell types, plays a crucial part in numerous cell mediated and humoral immune reactions that may be of pathogenetic importance in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). To further evaluate the pathogenetic role of CD40L in RA, expression of CD40L and various other T cell activation antigens as well as costimulatory molecules was investigated on CD4+ T cells in RA by flow cytometry.
Methods: Two colour flow cytometry was used to determine the percentage of CD4+ T cells expressing CD40L, CD69, CD25, HLA-DR, CD39, CD27 and CD28 in peripheral blood (PB) of 62 RA patients in comparison to 20 healthy controls (HC). Disease activity was assessed by clinical, laboratory and radiological examination. Status of clinical remission of RA was evaluated according to the ACR preliminary criteria for complete clinical remission of RA.
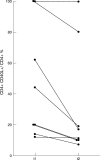
Results: CD40L was expressed on > 10% of CD4+ T cells in 29% of RA patients thus defining a CD40L(high+) patient group. Disease activity as estimated by C reactive protein, rheumatoid factor and status of clinical remission of disease (p = 0.049) was higher in this subgroup than in the RA CD40L(low+) group. Expression of CD69, CD25, and HLA-DR was significantly increased in both RA patient groups in comparison with HC. However, the percentage of CD39+ CD4+ T cells was increased only in the RA CD40L(high+) subgroup (versus HC p = 0.019, versus RA CD40L(low+) p = 0.044). Furthermore, expression of CD40L and CD39 on CD4+ T cells correlated positively as estimated by Spearman rank correlation (p<0.001). The percentage of CD4+ T cells lacking the costimulatory molecules CD27 (p = 0.002) and CD28 (p = 0.026) was increased in RA CD40L(low+) patients in comparison with HC.
Conclusions: These data suggest that increased expression of CD40L on CD4+ T cells in RA indicates prolonged and increased activation of CD4+ T lymphocytes and is associated with active disease and possibly an unfavourable prognosis. Whether this phenotypically defined RA CD40L(high+) subgroup will preferentially respond to an anti-CD40L antibody treatment remains to be elucidated.
Figures
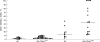


Similar articles
-
[Detection of peripheral follicular helper T cells in rheumatoid arthritis].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Dec 18;48(6):951-957. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 27987496 Chinese.
-
Autoimmune thrombocytopenia: flow cytometric determination of platelet-associated CD154/CD40L and CD40 on peripheral blood T and B lymphocytes.Hematology. 2007 Aug;12(4):301-7. doi: 10.1080/10245330701383957. Hematology. 2007. PMID: 17654056
-
Assessment of CD40 and CD40L expression in rheumatoid arthritis patients, association with clinical features and DAS28.Clin Exp Med. 2019 Nov;19(4):427-437. doi: 10.1007/s10238-019-00568-5. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31313080
-
The role of CD40 ligand in costimulation and T-cell activation.Immunol Rev. 1996 Oct;153:85-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1996.tb00921.x. Immunol Rev. 1996. PMID: 9010720 Review.
-
Leveraging blood and tissue CD4+ T cell heterogeneity at the single cell level to identify mechanisms of disease in rheumatoid arthritis.Curr Opin Immunol. 2017 Dec;49:27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2017.08.005. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28888129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The 3'-UTR (CA)n microsatellite on CD40LG gene as a possible genetic marker for rheumatoid arthritis in Mexican population: impact on CD40LG mRNA expression.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Feb;37(2):345-353. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3853-9. Epub 2017 Sep 30. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 28963582
-
High expression of the ectonucleotidase CD39 on T cells from the inflamed site identifies two distinct populations, one regulatory and one memory T cell population.J Immunol. 2010 Jul 1;185(1):134-43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803474. Epub 2010 May 24. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20498355 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsies to guide therapeutic decisions in rheumatoid arthritis.Transl Res. 2018 Nov;201:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 30092207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single rising doses of BI 655064, an antagonistic anti-CD40 antibody in healthy subjects: a potential novel treatment for autoimmune diseases.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Feb;74(2):161-169. doi: 10.1007/s00228-017-2362-8. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29127458 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of BI 655064, an antagonistic anti-CD40 antibody, on clinical and biomarker variables in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIa study.Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Jun;78(6):754-760. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214729. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 30902820 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

