Expression of regeneration and tolerance factor correlates directly with human immunodeficiency virus infection and inversely with hepatitis C virus infection
- PMID: 10702493
- PMCID: PMC95849
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.7.2.200-205.2000
Expression of regeneration and tolerance factor correlates directly with human immunodeficiency virus infection and inversely with hepatitis C virus infection
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) cause two of the most prevalent debilitating viral infections. HIV appears to induce a skewing toward a Th2 response, while in HCV infection a Th1 response appears to dominate. Regeneration and tolerance factor (RTF) may participate in driving or sustaining a Th2 cytokine response. The expression of RTF on CD3(+) T cells of HIV-seropositive (HIV(+)) individuals is increased. The purpose of this study was to compare the expression of RTF during HIV infections with that during HCV infections. Three-color flow-cytometric analysis of peripheral blood collected from HIV(+) HCV-seropositive (HCV(+)), HIV- and HCV-seropositive (HIV(+) HCV(+)), and HIV- and HCV-seronegative (HIV(-) HCV(-)) individuals was performed. Levels of RTF expression on T-lymphocyte subsets from these groups were compared, as were levels of RTF expression on activated T cells expressing CD38 and HLA-DR, to determine the relationship of RTF expression to these infections. We demonstrated that the expression of RTF on surfaces of T cells from HIV(+) individuals is upregulated and that its expression on T cells from HCV(+) individuals is downregulated. A twofold increase in the mean channel fluorescence of RTF on CD3(+) T cells was seen in both HIV(+) and HIV(+) HCV(+) individuals compared to HIV(-) HCV(-) individuals. HCV(+) individuals had lower levels of RTF expression than HIV(-) HCV(-) individuals (P < 0.005 for CD4(+); P < 0.0005 for CD8(+)). In terms of percentages of T cells expressing RTF, the groups were ranked as follows: HIV(+) > HIV(+) HCV(+) > HIV(-) HCV(-) > HCV(+). The results indicate that RTF expression correlates with HIV-associated immune activation and may be associated with Th2-type responses.
Figures
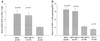


Similar articles
-
Expression of a novel protein by regenerating hepatocytes and peripheral blood lymphocytes.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001 Nov;8(6):1292-4. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.8.6.1292-1294.2001. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11687481 Free PMC article.
-
Regeneration and tolerance factor: a correlate of human immunodeficiency virus-associated T-cell activation.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999 Nov;6(6):872-7. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.6.6.872-877.1999. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10548579 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1-specific cytolytic T-lymphocyte activity correlates with lower viral load, higher CD4 count, and CD8+CD38-DR- phenotype: comparison of statistical methods for measurement.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1999 Sep 1;22(1):19-30. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199909010-00003. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1999. PMID: 10534143
-
Role of CD38 in HIV-1 infection: an epiphenomenon of T-cell activation or an active player in virus/host interactions?AIDS. 2000 Jun 16;14(9):1079-89. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200006160-00004. AIDS. 2000. PMID: 10894271 Review. No abstract available.
-
CD38+CD8+ T cells as a marker of poor response to therapy in HIV-infected individuals.Chem Immunol. 2000;75:207-17. doi: 10.1159/000058770. Chem Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10851786 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Expression of a novel protein by regenerating hepatocytes and peripheral blood lymphocytes.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001 Nov;8(6):1292-4. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.8.6.1292-1294.2001. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11687481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beaman K D, Angkachatchai V, Gilman-Sachs A. TJ6: the pregnancy-associated cytokine. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1996;35:338–341. - PubMed
-
- Beaman K D, Hoversland R C. Induction of abortion in mice with a monoclonal antibody specific for suppressor T-lymphocyte molecules. J Reprod Fertil. 1988;82:691–696. - PubMed
-
- Beld M, Penning M, Lukashov V, McMorrow M, Roos M, Pakker N, van den Hoek A, Goudsmit J. Evidence that both HIV and HIV-induced immunodeficiency enhance HCV replication among HCV seroconverters. Virology. 1998;244:504–512. - PubMed
-
- Chaouat G, Meliani A A, Martal J, Raghupathy A, Elliot J, Mosmann T, Wegmann T G. IL-10 prevents naturally occurring fetal loss in the CBA × DBA/2 mating combination, and local defect in IL-10 production in this abortion-prone combination is corrected by in vivo injection of IFN-γ. J Immunol. 1995;154:4261–4268. - PubMed
-
- Clerici M, Shearer G M. The Th1-Th2 switch is a critical step in the etiology of HIV infection. Immunol Today. 1993;14:107–110. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

