Membrane topology and insertion of membrane proteins: search for topogenic signals
- PMID: 10704472
- PMCID: PMC98984
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.64.1.13-33.2000
Membrane topology and insertion of membrane proteins: search for topogenic signals
Abstract
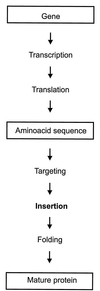
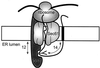
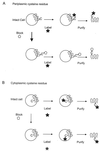
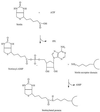
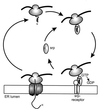
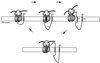
Integral membrane proteins are found in all cellular membranes and carry out many of the functions that are essential to life. The membrane-embedded domains of integral membrane proteins are structurally quite simple, allowing the use of various prediction methods and biochemical methods to obtain structural information about membrane proteins. A critical step in the biosynthetic pathway leading to the folded protein in the membrane is its insertion into the lipid bilayer. Understanding of the fundamentals of the insertion and folding processes will significantly improve the methods used to predict the three-dimensional membrane protein structure from the amino acid sequence. In the first part of this review, biochemical approaches to elucidate membrane protein topology are reviewed and evaluated, and in the second part, the use of similar techniques to study membrane protein insertion is discussed. The latter studies search for signals in the polypeptide chain that direct the insertion process. Knowledge of the topogenic signals in the nascent chain of a membrane protein is essential for the evaluation of membrane topology studies.
Figures

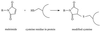

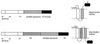

References
-
- Akabas M H, Karlin A. Identification of acetylcholine receptor channel-lining residues in the M1 segment of the alpha-subunit. Biochemistry. 1995;34:12496–12500. - PubMed
-
- Akabas M H, Kaufmann C, Archdeacon P, Karlin A. Identification of acetylcholine receptor channel-lining residues in the entire M2 segment of the alpha subunit. Neuron. 1994;13:919–927. - PubMed
-
- Akabas M H, Kaufmann C, Cook T A, Archdeacon P. Amino acid residues lining the chloride channel of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:14865–14868. - PubMed
-
- Akabas M H, Stauffer D A, Xu M, Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor channel structure probed in cysteine-substitution mutants. Science. 1992;258:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama Y, Ito K. Folding and assembly of bacterial alkaline phosphatase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:8146–8150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

