Axonal transport of microtubule-associated protein 1B (MAP1B) in the sciatic nerve of adult rat: distinct transport rates of different isoforms
- PMID: 10704485
- PMCID: PMC6772501
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-06-02112.2000
Axonal transport of microtubule-associated protein 1B (MAP1B) in the sciatic nerve of adult rat: distinct transport rates of different isoforms
Abstract
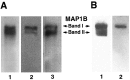
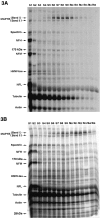
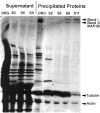
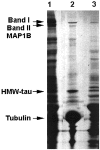
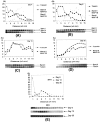
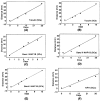
Cytoskeletal proteins are axonally transported with slow components a and b (SCa and SCb). In peripheral nerves, the transport velocity of SCa, which includes neurofilaments and tubulin, is 1-2 mm/d, whereas SCb, which includes actin, tubulin, and numerous soluble proteins, moves as a heterogeneous wave at 2-4 mm/d. We have shown that two isoforms of microtubule-associated protein 1B (MAP1B), which can be separated on SDS polyacrylamide gels on the basis of differences in their phosphorylation states (band I and band II), were transported at two different rates. All of band I MAP1B moved as a coherent wave at a velocity of 7-9 mm/d, distinct from slow axonal transport components SCa and SCb. Several other proteins were detected within the component that moved at the velocity of 7-9 mm/d, including the leading wave of tubulin and actin. The properties of this component define a distinct fraction of the slow axonal transport that we suggest to term slow component c (SCc). The relatively fast transport of the phosphorylated MAP1B isoform at 7-9 mm/d may account for the high concentration of phosphorylated MAP1B in the distal end of growing axons. In contrast to band I MAP1B, the transport profile of band II was complex and contained components moving with SCa and SCb and a leading edge at SCc. Thus, MAP1B isoforms in different phosphorylation states move with distinct components of slow axonal transport, possibly because of differences in their abilities to associate with other proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Baas PW, Yu W. A composite model for establishing the microtubule arrays of the neuron. Mol Neurobiol. 1996;12:145–161. - PubMed
-
- Bamburg JR, Bray D, Chapman K. Assembly of microtubules at the tip of growing axons. Nature. 1986;321:788–790. - PubMed
-
- Black MM, Lasek RJ. A difference between the proteins conveyed in the fast component of axonal transport in guinea pig hypoglossal and vagus motor neurons. J Neurobiol. 1978;9:433–443. - PubMed
-
- Black MM, Lasek RJ. Axonal transport of actin: slow component b is the principal source of actin for the axon. Brain Res. 1979;171:401–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
