Regulation of kinetic properties of GluR2 AMPA receptor channels by alternative splicing
- PMID: 10704491
- PMCID: PMC6772485
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-06-02166.2000
Regulation of kinetic properties of GluR2 AMPA receptor channels by alternative splicing
Abstract
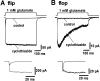
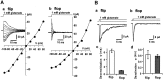
The four subunits of the AMPA-type glutamate receptor (GluR1-GluR4 or GluR-A-GluR-D) exist in two distinct forms, flip and flop, generated by alternative splicing of a 115 bp region. The GluR2 subunit plays a key role in determining the functional properties of the AMPA receptor channel. In this study, we examined the differences in kinetic properties between the flip and flop splice variants of the GluR2 subunit expressed in Xenopus oocytes using fast agonist application techniques. Glutamate was applied to outside-out patches from oocytes with piezo-driven double-barreled application pipettes. Because homomeric receptor channels composed of the edited form of GluR2 (GluR2R) produce no appreciable current responses, we expressed the unedited form of GluR2 (GluR2Q) in oocytes, which produced large current responses sufficient for analysis of the kinetic properties. The time constant for desensitization during application of 1 mM glutamate was 5.89 +/- 0. 17 msec (n = 50) in flip and 1.18 +/- 0.05 msec (n = 37) in flop. The deactivation time constant was 0.62 +/- 0.06 msec (n = 10) in flip and 0.54 +/- 0.05 msec (n = 10) in flop. The steady-state nondesensitizing current was 6.8 +/- 0.4% (n = 53) of the peak current in flip, whereas it was almost negligible in flop, being only 1.1 +/- 0.1% (n = 36). The slower desensitization kinetics and larger steady-state current responses in the flip variant were also observed in heteromeric receptors assembled from GluR2Q/GluR2R. Thus, desensitization occurred much more prominently in the flop variant in the recombinant GluR2 receptor channels.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Differential modulation of AMPA receptors by cyclothiazide in two types of striatal neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2000 Aug;12(8):2871-80. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00175.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10971630
-
Characterization of AMPA receptors on isolated amacrine-like cells in carp retina.Eur J Neurosci. 1999 Dec;11(12):4233-40. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00851.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10594649
-
Control of kinetic properties of GluR2 flop AMPA-type channels: impact of R/G nuclear editing.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Jan;15(1):51-62. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01841.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11860506
-
AMPA receptor potentiators for the treatment of CNS disorders.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004 Jun;3(3):181-94. doi: 10.2174/1568007043337508. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004. PMID: 15180479 Review.
-
LY404187: a novel positive allosteric modulator of AMPA receptors.CNS Drug Rev. 2002 Fall;8(3):255-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2002.tb00228.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2002. PMID: 12353058 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ionotropic glutamate receptor mRNA editing in the prefrontal cortex: no alterations in schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012 Jul;37(4):267-72. doi: 10.1503/jpn.110107. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22469055 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA receptor current density, not desensitization, predicts selective motoneuron vulnerability.J Neurosci. 2000 Oct 1;20(19):7158-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-19-07158.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11007871 Free PMC article.
-
A charge-inverting mutation in the "linker" region of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors alters agonist binding and gating kinetics independently of allosteric modulators.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 11;289(15):10702-10714. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526921. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24550387 Free PMC article.
-
Block of AMPA receptor desensitization by a point mutation outside the ligand-binding domain.J Neurosci. 2004 May 19;24(20):4728-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0757-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15152033 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying developmental speeding in AMPA-EPSC decay time at the calyx of Held.J Neurosci. 2005 Jan 5;25(1):199-207. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3861-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15634782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong N, Sun Y, Chen G-Q, Gouaux E. Structure of a glutamate receptor ligand-binding core in complex with kainate. Nature. 1998;395:913–917. - PubMed
-
- Bochet P, Audinat E, Lambolez B, Crépel F, Rossier J, Iino M, Tsuzuki K, Ozawa S. Subunit composition at the single-cell level explains functional properties of a glutamate-gated channel. Neuron. 1994;12:383–388. - PubMed
-
- Boulter J, Hollmann M, O'Shea-Greenfield A, Hartley M, Deneris E, Maron C, Heinemann S. Molecular cloning and functional expression of glutamate receptor subunit genes. Science. 1990;249:1033–1037. - PubMed
-
- Bowie D, Mayer M. Inward rectification of both AMPA and kainate subtype glutamate receptors generated by polyamine-mediated ion channel block. Neuron. 1995;15:453–462. - PubMed
-
- Burnashev N, Monyer H, Seeburg PH, Sakmann B. Divalent ion permeability of AMPA receptor channels is dominated by the edited form of a single subunit. Neuron. 1992;8:189–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
