Distinct roles for ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors in the maturation of excitatory synapses
- PMID: 10704498
- PMCID: PMC6772494
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-06-02229.2000
Distinct roles for ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors in the maturation of excitatory synapses
Abstract
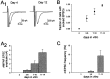
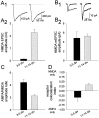
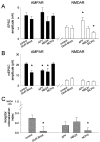
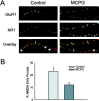
We used the single-cell culture preparation to study the role of activity in the development of glutamatergic synapses in vitro. Rat hippocampal cells grown in isolation on glial islands formed functional autaptic connections and continued to elaborate new synapses throughout the 2 week investigation, resulting in increases in both the evoked AMPA receptor (AMPAR) and NMDA receptor (NMDAR) components of the EPSC. Synaptogenesis was not prevented by chronic blockade of sodium channels or all of the known glutamate receptors. Analysis of miniature EPSCs revealed that AMPAR quantal size doubled over time in vitro whereas NMDAR quantal size remained constant. However, the proportion of synaptic responses mediated only by NMDARs increased over time in vitro. The increase in AMPAR quantal size was prevented by TTX and ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists, whereas the increase in the proportion of NMDAR-only synapses was prevented by metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists. Notably, chronic NMDAR blockade incubation did not block the formation of the AMPAR EPSC, indicating that NMDAR-dependent plasticity is not necessary for the onset of AMPAR synaptic transmission in this system. We conclude that action potentials and ionotropic glutamate receptor activation are necessary for the developmental increase in AMPAR quantal size and that metabotropic glutamate receptor activation is required for the production of NMDAR-only synapses, but none of these is essential for synapse formation.
Figures

References
-
- Allen CN, Brady R, Swann J, Hori N, Carpenter DO. N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are inactivated by trypsin. Brain Res. 1988;458:147–150. - PubMed
-
- Bekkers JM, Stevens CF. NMDA and non-NMDA receptors are co-localized at individual excitatory synapses in cultured rat hippocampus. Nature. 1989;341:230–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
