Reovirus-induced apoptosis requires activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB
- PMID: 10708412
- PMCID: PMC111796
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.7.2981-2989.2000
Reovirus-induced apoptosis requires activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB
Abstract
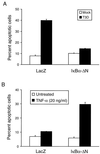
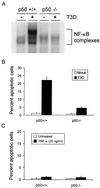
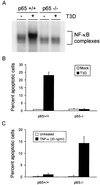
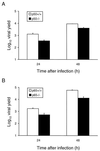
Reovirus infection induces apoptosis in cultured cells and in vivo. To identify host cell factors that mediate this response, we investigated whether reovirus infection alters the activation state of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB). As determined in electrophoretic mobility shift assays, reovirus infection of HeLa cells leads to nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB complexes containing Rel family members p50 and p65. Reovirus-induced activation of NF-kappaB DNA-binding activity correlated with the onset of NF-kappaB-directed transcription in reporter gene assays. Three independent lines of evidence indicate that this functional form of NF-kappaB is required for reovirus-induced apoptosis. First, treatment of reovirus-infected HeLa cells with a proteasome inhibitor prevents NF-kappaB activation following infection and substantially diminishes reovirus-induced apoptosis. Second, transient expression of a dominant-negative form of IkappaB that constitutively represses NF-kappaB activation significantly reduces levels of apoptosis triggered by reovirus infection. Third, mutant cell lines deficient for either the p50 or p65 subunits of NF-kappaB are resistant to reovirus-induced apoptosis compared with cells expressing an intact NF-kappaB signaling pathway. These findings indicate that NF-kappaB plays a significant role in the mechanism by which reovirus induces apoptosis in susceptible host cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IkappaB kinase subunits alpha and gamma are required for activation of NF-kappaB and induction of apoptosis by mammalian reovirus.J Virol. 2007 Feb;81(3):1360-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01860-06. Epub 2006 Nov 22. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17121808 Free PMC article.
-
Organ-specific roles for transcription factor NF-kappaB in reovirus-induced apoptosis and disease.J Clin Invest. 2005 Sep;115(9):2341-50. doi: 10.1172/JCI22428. Epub 2005 Aug 11. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16100570 Free PMC article.
-
Two distinct phases of virus-induced nuclear factor kappa B regulation enhance tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in virus-infected cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 16;278(20):18092-100. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300265200. Epub 2003 Mar 13. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12637521
-
Reovirus receptors, cell entry, and proapoptotic signaling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;790:42-71. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-7651-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23884585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral and cellular determinants of apoptosis induced by mammalian reovirus.Int Rev Immunol. 2003 Sep-Dec;22(5-6):477-503. doi: 10.1080/08830180305212. Int Rev Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12959755 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytidine Monophosphate N-Acetylneuraminic Acid Synthetase and Solute Carrier Family 35 Member A1 Are Required for Reovirus Binding and Infection.J Virol. 2020 Dec 22;95(2):e01571-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01571-20. Print 2020 Dec 22. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 33087464 Free PMC article.
-
Reovirus-induced G(2)/M cell cycle arrest requires sigma1s and occurs in the absence of apoptosis.J Virol. 2000 Oct;74(20):9562-70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.20.9562-9570.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11000227 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB Signaling in Targeting Tumor Cells by Oncolytic Viruses-Therapeutic Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Nov 8;10(11):426. doi: 10.3390/cancers10110426. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30413032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enter the kill zone: initiation of death signaling during virus entry.Virology. 2011 Mar 15;411(2):316-24. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.12.043. Epub 2011 Jan 22. Virology. 2011. PMID: 21262519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of NF-kappa B activity and cFLIP expression contribute to viral-induced apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2005 May;10(3):513-24. doi: 10.1007/s10495-005-1881-4. Apoptosis. 2005. PMID: 15909114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbadie C, Kabrun N, Bouali F, Vandenbunder B, Enrietto P. High levels of c-rel expression are associated with programmed cell death in the developing avian embryo and in bone marrow cells in vitro. Cell. 1993;75:899–912. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit V M. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science. 1998;281:1305–1308. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P, Baltimore D. IκB: a specific inhibitor of the NF-κB transcription factor. Science. 1988;242:540–546. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P, Baltimore D. A 65-kD subunit of active NF-κB is required for inhibition of NF-κB by IκB. Genes Dev. 1989;3:1689–1698. - PubMed
-
- Ballard D W, Bohnlein E, Lowenthal J W, Wano Y, Franza B R, Greene W C. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the kappa B element in the IL-2 receptor alpha gene. Science. 1988;241:1652–1655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

