Evidence for budding of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 selectively from glycolipid-enriched membrane lipid rafts
- PMID: 10708443
- PMCID: PMC111827
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.7.3264-3272.2000
Evidence for budding of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 selectively from glycolipid-enriched membrane lipid rafts
Abstract
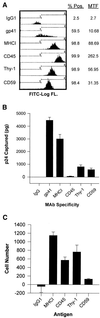
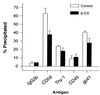
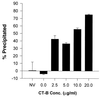
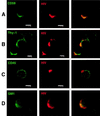
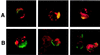
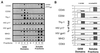
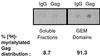
A number of recent studies have demonstrated the significance of detergent-insoluble, glycolipid-enriched membrane domains or lipid rafts, especially in regard to activation and signaling in T lymphocytes. These domains can be viewed as floating rafts composed of sphingolipids and cholesterol which sequester glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked proteins, such as Thy-1 and CD59. CD45, a 200-kDa transmembrane phosphatase protein, is excluded from these domains. We have found that human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) particles produced by infected T-cell lines acquire the GPI-linked proteins Thy-1 and CD59, as well as the ganglioside GM1, which is known to partition preferentially into lipid rafts. In contrast, despite its high expression on the cell surface, CD45 was poorly incorporated into virus particles. Confocal fluorescence microscopy revealed that HIV-1 proteins colocalized with Thy-1, CD59, GM1, and a lipid raft-specific fluorescent lipid, DiIC(16)(3), in uropods of infected Jurkat cells. CD45 did not colocalize with HIV-1 proteins and was excluded from uropods. Dot immunoassay of Triton X-100-extracted membrane fractions revealed that HIV-1 p17 matrix protein and gp41 were present in the detergent-resistant fractions and that [(3)H]myristic acid-labeled HIV Gag showed a nine-to-one enrichment in lipid rafts. We propose a model for the budding of HIV virions through lipid rafts whereby host cell cholesterol, sphingolipids, and GPI-linked proteins within these domains are incorporated into the viral envelope, perhaps as a result of preferential sorting of HIV Gag to lipid rafts.
Figures
References
-
- Arni S, Ilangumaran S, van Echten-Deckert G, Sandhoff K, Poincelet M, Briol A, Rungger-Brandle E, Hoessli D C. Differential regulation of Src-family protein tyrosine kinases in GPI domains of T lymphocyte plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;225:801–807. - PubMed
-
- Arthur L O, Bess J W J, Sowder R C, Benveniste R E, Mann D L, Cherman J-C, Henderson L E. Cellular proteins bound to immunodeficiency viruses: implication for pathogenesis and vaccines. Science. 1992;258:1935–1938. - PubMed
-
- Barclay A N, Beyers A D, Birkeland M L, Brown M H, Davis S J, Somoza C, Williams A F. The leukocyte antigen facts book. New York, N.Y: Academic Press; 1993.
-
- Cinek T, Horejsi V. The nature of large noncovalent complexes containing glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane glycoproteins and protein tyrosine kinases. J Immunol. 1992;149:2262–2270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

