The gastric H,K-ATPase blocker lansoprazole is an inhibitor of chloride channels
- PMID: 10711360
- PMCID: PMC1571856
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703070
The gastric H,K-ATPase blocker lansoprazole is an inhibitor of chloride channels
Abstract
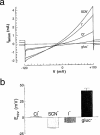
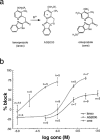
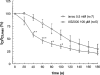
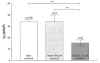
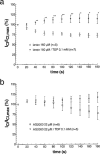
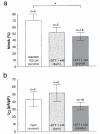
1. It was postulated that swelling dependent chloride channels are involved in the proton secretion of parietal cells. Since omeprazole, lansoprazole and its acid activated sulphenamide form AG2000 are structurally related to phenol derivatives known to block swelling dependent chloride channels, we set out to test, whether these substances--which are known to block the H,K-ATPase--could also lead to an inhibition of swelling-dependent chloride channels. Swelling-dependent chloride channels--characterized in many different cell types--show highly conserved biophysical and pharmacological features, therefore we investigated the effect of omeprazole, lansoprazole and its acid activated sulphenamide form AG2000 on swelling-dependent chloride channels elicited in fibroblasts, after the reduction of the extracellular osmolarity. 2. Omeprazole, lansoprazole and its acid activated sulphenamide form AG2000 are able to block swelling-dependent chloride channels (IClswell). 3. Lansoprazole and its protonated metabolite AG2000 act on at least two different sites of the IClswell protein: on an extracellular site which seems to be in a functional proximity to the nucleotide binding site, and on an intracellular site which allows the formation of disulfide-bridges. 4. The inhibition of the proton pump and the simultaneous blocking of chloride channels by omeprazole, lansoprazole and its acid activated sulphenamide form AG2000, as described here could be an effective mode to restrict proton secretion in parietal cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Restoration of acid secretion following treatment with proton pump inhibitors.Gastroenterology. 2002 Nov;123(5):1588-97. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.36593. Gastroenterology. 2002. PMID: 12404233
-
Sites of reaction of the gastric H,K-ATPase with extracytoplasmic thiol reagents.J Biol Chem. 1997 Sep 5;272(36):22438-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.36.22438. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9278394
-
Proton pump inhibitors: new drugs and indications.Am Fam Physician. 1996 Jan;53(1):285-92. Am Fam Physician. 1996. PMID: 8546054 Review.
-
Characterization of the inhibitory activity of tenatoprazole on the gastric H+,K+ -ATPase in vitro and in vivo.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Mar 14;71(6):837-49. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.11.030. Epub 2006 Jan 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16405921
-
Lansoprazole: a comprehensive review.Pharmacotherapy. 1997 Mar-Apr;17(2):308-26. Pharmacotherapy. 1997. PMID: 9085323 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunobiological effects of lipopolysaccharide derived from Helicobacter pylori and influence of a proton pump inhibitor lansoprazole on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2024 Dec;69(6):1369-1378. doi: 10.1007/s12223-024-01188-7. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2024. PMID: 39153156 Free PMC article.
-
The proton pump inhibitor lansoprazole improves the skeletal phenotype in dystrophin deficient mdx mice.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 2;8(7):e66617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066617. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23843959 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and Metabolic Responses Triggered by Omeprazole Improve Tomato Plant Tolerance to NaCl Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Feb 27;9:249. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00249. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29535755 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide CRISPR screens identify CLC-2 as a drug target for anti-herpesvirus therapy: tackling herpesvirus drug resistance.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Feb;68(2):515-526. doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2627-8. Epub 2024 Oct 12. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39428427
-
Oral proton pump inhibitors disrupt horizontal cell-cone feedback and enhance visual hallucinations in macular degeneration patients.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Feb 27;54(2):1485-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-11091. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23341015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ASANO S., INOIE M., TAKEGUCHI N. The Cl-channel in Hog Gastric Vesicles is Part of the Function of H,K-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 1987;262:13263–13268. - PubMed
-
- BARRADELL L.B., FAULDS D., MCTAVISH D. Lansoprazole. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and its therapeutic efficacy in acid related disorders. Drugs. 1992;44:225–250. - PubMed
-
- CUPPOLETTI J., BAKER A.M., MALINOWSKA D.H. Cl-channels of the gastric parietal cell that are active at low pH. Am. J. Physiol. 1993;264:C1609–C1618. - PubMed
-
- CUPPOLETTI J., SACHS G. Regulation of Gastric Acid Secretion via Modulation of a Chloride Conductance. J. Biol. Chem. 1984;259:14952–14959. - PubMed
-
- DEMAREST J.R., LOO D.F., SACHS G. Activation of Apical Chloride Channels in the Gastric Oxyntic Cell. Science. 1989;245:402–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

