Proteomics of the chloroplast: systematic identification and targeting analysis of lumenal and peripheral thylakoid proteins
- PMID: 10715320
- PMCID: PMC139834
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.12.3.319
Proteomics of the chloroplast: systematic identification and targeting analysis of lumenal and peripheral thylakoid proteins
Abstract
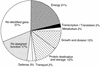
The soluble and peripheral proteins in the thylakoids of pea were systematically analyzed by using two-dimensional electrophoresis, mass spectrometry, and N-terminal Edman sequencing, followed by database searching. After correcting to eliminate possible isoforms and post-translational modifications, we estimated that there are at least 200 to 230 different lumenal and peripheral proteins. Sixty-one proteins were identified; for 33 of these proteins, a clear function or functional domain could be identified, whereas for 10 proteins, no function could be assigned. For 18 proteins, no expressed sequence tag or full-length gene could be identified in the databases, despite experimental determination of a significant amount of amino acid sequence. Nine previously unidentified proteins with lumenal transit peptides are presented along with their full-length genes; seven of these proteins possess the twin arginine motif that is characteristic for substrates of the TAT pathway. Logoplots were used to provide a detailed analysis of the lumenal targeting signals, and all nuclear-encoded proteins identified on the two-dimensional gels were used to test predictions for chloroplast localization and transit peptides made by the software programs ChloroP, PSORT, and SignalP. A combination of these three programs was found to provide a useful tool for evaluating chloroplast localization and transit peptides and also could reveal possible alternative processing sites and dual targeting. The potential of proteomics for plant biology and homology-based searching with mass spectrometry data is discussed.
Figures
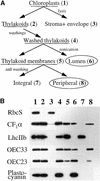
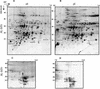

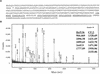

Comment in
-
Proteomics: broad strokes of expressionism?Plant Cell. 2000 Mar;12(3):303-4. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.3.303. Plant Cell. 2000. PMID: 10715314 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adam, Z. (1996). Protein stability and degradation in chloroplasts. Plant Mol. Biol. 32 773–783. - PubMed
-
- Bauw, G., De Loose, M., Inzé, D., van Montagu, M., and Vandekerckhove, J. (1987). Alterations in the phenotype of plant cells studied by NH2-terminal amino acid–sequence analysis of proteins electroblotted from two-dimensional gel-separated total extracts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84 4806–4810. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belanger, F.C., Leustek, T., Chu, B., and Kriz, A.L. (1995). Evidence for the thiamine biosynthetic pathway in higher-plant plastids and its developmental regulation. Plant Mol. Biol. 29 809–821. - PubMed
-
- Bevan, M., et al., (1998). Analysis of 1.9 Mb of contiguous sequence from chromosome 4 of Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 39 485–488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

