Severe B cell hyperplasia and autoimmune disease in TALL-1 transgenic mice
- PMID: 10716715
- PMCID: PMC16246
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.7.3370
Severe B cell hyperplasia and autoimmune disease in TALL-1 transgenic mice
Abstract
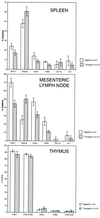
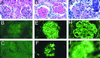
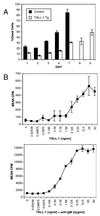
TALL-1/Blys/BAFF is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand superfamily that is functionally involved in B cell proliferation. Here, we describe B cell hyperplasia and autoimmune lupus-like changes in transgenic mice expressing TALL-1 under the control of a beta-actin promoter. The TALL-1 transgenic mice showed severe enlargement of spleen, lymph nodes, and Peyer's patches because of an increased number of B220+ cells. The transgenic mice also had hypergammaglobulinemia contributed by elevations of serum IgM, IgG, IgA, and IgE. In addition, a phenotype similar to autoimmune lupus-like disease was also seen in TALL-1 transgenic mice, characterized by the presence of autoantibodies to nuclear antigens and immune complex deposits in the kidney. Prolonged survival and hyperactivity of transgenic B cells may contribute to the autoimmune lupus-like phenotype in these animals. Our studies further confirm TALL-1 as a stimulator of B cells that affect Ig production. Thus, TALL-1 may be a primary mediator in B cell-associated autoimmune diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Smith C A, Farrah T, Goodwin R G. Cell. 1994;76:959–962. - PubMed
-
- Lacey D L, Timms E, Tan H-L, Kelley M J, Dunstan C R, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S, et al. Cell. 1998;93:165–176. - PubMed
-
- Chichepotiche Y, Bourdon P R, Xu J, Hsu Y M, Scott H, Hession C, Garcia I, Browning J L. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32401–32410. - PubMed
-
- Mauri D N, Ebner R, Montgomery R I, Kochel R I, Cheung T C, Yu G L, Ruben S, Murphy M, Eisenberg R J, Cohen G H, et al. Immunity. 1998;8:21–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

