Connecting oxidative stress, auxin, and cell cycle regulation through a plant mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
- PMID: 10716978
- PMCID: PMC33972
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.6.2405
Connecting oxidative stress, auxin, and cell cycle regulation through a plant mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
Figures
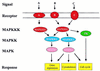
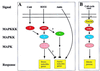
Comment on
-
Functional analysis of oxidative stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Mar 14;97(6):2940-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.6.2940. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10717008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Widmann C, Gibson S, Jarpe M B, Johnson G L. Phys Rev. 1999;79:143–180. - PubMed
-
- Ligterink, W. & Hirt, H. (2000) Int. Rev. Cytol., in press. - PubMed
-
- Whitmarsh A J, Davis R J. Trends Biochem Sci. 1998;23:481–485. - PubMed
-
- Lamb C, Dixon R A. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1997;48:251–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

