Interleukin-4 receptor alpha-deficient BALB/c mice show an unimpaired T helper 2 polarization in response to Leishmania major infection
- PMID: 10722563
- PMCID: PMC97347
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.4.1773-1780.2000
Interleukin-4 receptor alpha-deficient BALB/c mice show an unimpaired T helper 2 polarization in response to Leishmania major infection
Abstract
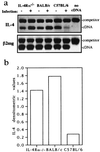
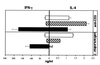
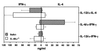
We recently generated interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptor alpha-deficient (IL-4Ralpha(-/-)) BALB/c mice and showed evidence for a protective role of IL-13-mediated functions in leishmaniasis. In this study, we investigated the IL-4 expression and T helper 2 (Th2) development in Leishmania major-infected IL-4Ralpha(-/-) mice. Here we show that the early burst of IL-4 expression observed in L. major-infected BALB/c mice is independent of IL-4Ralpha-mediated functions. Subsequently, we confirmed an impaired Th2 development in vitro. Unexpectedly, during L. major infection, isolated CD4(+) IL-4Ralpha(-/-) T cells expressed high IL-4- but low gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-specific mRNA, comparable to Th2-polarized BALB/c CD4(+) cells and in contrast to Th1-polarized C57BL/6 CD4(+) cells. Since antigen-specific restimulated popliteal lymph node cells (PLN) of IL-4Ralpha(-/-) mice also responded with high IL-4 but low IFN-gamma production, comparable to Th2-polarized cells from wild-type BALB/c mice and in contrast to Th1-polarized C57BL/6 cells, these results suggested an unimpaired Th2 polarization during an established infection with L. major. To further define the observed IL-4 receptor-independent Th2 cell phenotype, we determined an independent Th2 marker, the IL-12 receptor beta-2 (IL-12Rbeta2)-specific transcript levels of CD4(+) T cells. Confirming Th2 polarization in L. major-infected IL-4Ralpha(-/-) mice, comparable IL-12Rbeta2 message levels between CD4(+) T cells from infected IL-4Ralpha(-/-) mice and Th2 cells from BALB/c mice were found, whereas Th1-polarized C57BL/6 cells showed strikingly increased IL-12Rbeta2 expression levels. These results indicate that signals mediated by the IL-4Ralpha are not necessary to induce and sustain an efficient IL-4 expression and Th2 polarization in L. major-infected BALB/c mice and suggest that IL-4Ralpha-independent mechanisms underlie the default Th2 development in L. major-infected BALB/c mice.
Figures

References
-
- Barner M, Mohrs M, Brombacher F, Kopf M. Differences between IL-4Rα and IL-4 deficient mice reveal a novel role of IL-13 in the regulation of T helper 2 cells and protection to nematode infection. Curr Biol. 1998;8:669–672. - PubMed
-
- Bogdan C, Gessner A, Rollinghoff M. Cytokines in leishmaniasis: a complex network of stimulatory and inhibitory interactions. Immunobiology. 1993;189:356–396. - PubMed
-
- Bouaboula M, Legoux P, Pessegue B, Delpech B, Dumont X, Piechaczyk M, Casellas P, Shire D. Standardization of mRNA titration using a polymerase chain reaction method involving co-amplification with a multispecific internal control. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:21830–21838. - PubMed
-
- Chatelain R, Mauze S, Varkila K, Coffman R L. Leishmania major infection in interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma depleted mice. Parasite Immunol. 1999;21:423–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

