Gamma interferon dominates the murine cytokine response to the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis and helps to control the degree of early rickettsemia
- PMID: 10722570
- PMCID: PMC97354
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.4.1827-1833.2000
Gamma interferon dominates the murine cytokine response to the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis and helps to control the degree of early rickettsemia
Abstract
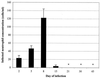
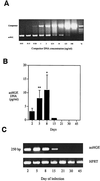
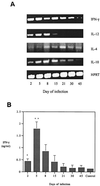
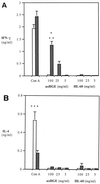
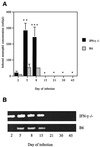
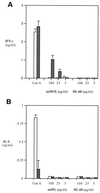
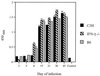
The cytokine response to the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis (HGE) was assessed in a murine infection model and the role of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), a cytokine that is crucial for host defenses against intracellular pathogens, was investigated by using IFN-gamma-deficient mice. The agent of HGE (aoHGE) is an obligate intracellular bacterium that survives within neutrophils: morulae (vacuoles containing HGE organisms) are evident in polymorphonuclear leukocytes of experimentally infected immunocompetent mice for 1 to 2 weeks. We now show that IFN-gamma levels increase during early infection of C3H/HeN or C57BL/6 mice with HGE bacteria. Moreover, in response to aoHGE extracts or concanavalin A, splenocytes from ehrlichia-infected mice produced more IFN-gamma and less interleukin-4 than controls, suggesting that aoHGE partially skewed the immune response towards a Th1 phenotype. Absolute concentration of morulae containing neutrophils in blood was 122 +/- 22 cells/microliter on day 8. The bacterial DNA burden was also highest on day 8 and then declined after IFN-gamma levels peaked. In contrast, IFN-gamma-deficient mice had a markedly elevated HGE bacteria burden with morulae concentration of 282 +/- 48 cells/microliter on day 5 (P = 0.004) and 242 +/- 63 cells/microliter on day 8 (P = 0.005). Rickettsemia resolved in immunocompetent and IFN-gamma deficient mice after 2 weeks, while both the immunocompetent and the IFN-gamma-deficient mice had increased serum antibodies against aoHGE antigens at this time point. These data demonstrate that the HGE agent elicits a prominent IFN-gamma response in mice and that IFN-gamma is important in controlling the degree of rickettsemia during the early phase of infection, while IFN-gamma independent mechanisms play a role at later time points.
Figures

References
-
- Abbas A, Murphy K M, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;383:787–793. - PubMed
-
- Adachi J A, Grimm E M, Johnson P, Uthman M, Kaplan B, Rakita R M. Human granulocytic ehrlichiosis in a renal transplant patient: case report and review of the literature. Transplantation. 1997;64:1139–1142. - PubMed
-
- Aguero-Rosenfeld M E, Horowitz H W, Wormser G P, McKenna D F, Nowakowski J, Munoz J, Dumler J S. Human granulocytic ehrlichiosis: a case series from a medical center in New York State. Ann Intern Med. 1996;125:904–908. - PubMed
-
- Anthony S J, Dumler J S, Hunter E. Human ehrlichiosis in a liver transplant recipient. Transplantation. 1995;60:879. - PubMed
-
- Bakken J S, Krueth J, Wilson-Nordskog C, Tilden R L, Asanovich K, Dumler J S. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis. JAMA. 1996;275:199–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

