Impact of siderophore production on Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in immunosuppressed mice
- PMID: 10722571
- PMCID: PMC97355
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.4.1834-1839.2000
Impact of siderophore production on Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in immunosuppressed mice
Abstract
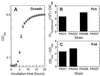
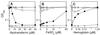
Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces siderophores, pyoverdin and pyochelin, for high-affinity iron uptake. To investigate their contribution to P. aeruginosa infections, we constructed allelic exchange mutants from strain PAO1 which were deficient in producing one or both of the siderophores. When inoculated into the calf muscles of immunosuppressed mice, pyochelin-deficient and pyoverdin-deficient mutants grew and killed the animals as efficiently as PAO1. In contrast, the pyochelin- and pyoverdin-deficient (double) mutant did not show lethal virulence, although it did infect the muscles. On the other hand, when inoculated intranasally, all mutants grew in the lungs and killed immunosuppressed mice. Compared with PAO1, however, the pyoverdin-deficient mutant and the double mutant grew poorly in the lungs, and the latter was significantly attenuated for virulence. Irrespective of the inoculation route, the pyoverdin-deficient and doubly deficient mutants detected in the blood were significantly less numerous than PAO1. Additionally, in vitro examination demonstrated that the growth of the double mutant was extremely reduced under a free-iron-restricted condition with apotransferrin but that the growth reduction was completely canceled by supplementation with hemoglobin as a heme source. These results suggest that both pyoverdin and pyochelin are required for efficient bacterial growth and full expression of virulence in P. aeruginosa infection, although pyoverdin may be comparatively more important for bacterial growth and dissemination. However, the siderophores were not always required for infection. It is possible that non-siderophore-mediated iron acquisition, such as via heme uptake, might also play an important role in P. aeruginosa infections.
Figures
References
-
- Bodey G P, Bolivar R, Fainstein V, Jadeja L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983;5:279–313. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

