Group B streptococci and other gram-positive cocci bind to cytokeratin 8
- PMID: 10722610
- PMCID: PMC97394
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.4.2129-2134.2000
Group B streptococci and other gram-positive cocci bind to cytokeratin 8
Abstract
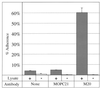
Group B streptococci (GBS) adhere to surface receptors present on epithelial cells; these receptors include fibronectin and laminin. To identify other possible receptors, plasma membranes from A549 cells, a respiratory tract epithelial cell line, were prepared. These plasma membranes were tested in a protein blot analysis using radiolabeled GBS as a probe. GBS adhered to two species, with molecular masses of 50 kDa (p50) and 57 kDa (p57). We concluded that p50 and p57 correspond to two forms of cytokeratin 8 (CK8) on the basis of the following results: (i) protein blot results demonstrated that p50 and p57 exactly comigrated with two forms of CK8 after separation by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE); (ii) p50 and p57 exactly comigrated with CK8 after separation by two-dimensional PAGE; (iii) CK8 in solution bound to GBS, as demonstrated by immunoblot analysis of proteins from A549 lysates that bound to GBS in a liquid-phase assay; and (iv) radiolabeled GBS bound to A549 lysate-derived CK8 that had been captured in anti-CK8-coated microtiter wells. CK8 bound to COH1-13, an acapsular mutant of COH1, demonstrating that adherence is not mediated by capsular polysaccharide. Trypsin-treated GBS did not bind to CK8, indicating that adherence is mediated via a protein on the surface of GBS. Soluble CK8 bound to six of six GBS strains tested. Soluble CK8 also bound to Staphylococcus aureus, Lactococcus lactis, Enterococcus faecalis, and Streptococcus pyogenes. We hypothesize that adherence of GBS to cytokeratin may be important for maintenance of colonization at sites of keratinized epithelium, such as the vagina, or for adherence of these bacteria to damaged epithelial cells at other sites.
Figures






References
-
- Baker C J, Edwards M S. Group B streptococcal infections. In: Remington J S, Klein J O, editors. Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant. 4th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: W. B. Saunders; 1994. pp. 980–1054.
-
- Capuco A V, Bright S A, Pankey J W, Wood D L, Miller R H, Bitman J. Increased susceptibility to intramammary infection following removal of teat canal keratin. J Dairy Sci. 1992;75:2126–2130. - PubMed
-
- Hembrough T A, Li L, Gonias S L. Cell-surface cytokeratin 8 is the major plasminogen receptor on breast cancer cells and is required for the accelerated activation of cell-associated plasminogen by tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:25684–25691. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

