gammadelta T cells are a component of early immunity against preerythrocytic malaria parasites
- PMID: 10722623
- PMCID: PMC97407
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.4.2224-2230.2000
gammadelta T cells are a component of early immunity against preerythrocytic malaria parasites
Abstract
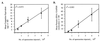
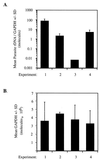
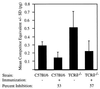
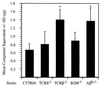
We tested the hypothesis that gammadelta T cells are a component of an early immune response directed against preerythrocytic malaria parasites that are required for the induction of an effector alphabeta T-cell immune response generated by irradiated-sporozoite (irr-spz) immunization. gammadelta T-cell-deficient (TCRdelta(-/-)) mice on a C57BL/6 background were challenged with Plasmodium yoelii (17XNL strain) sporozoites, and then liver parasite burden was measured at 42 h postchallenge. Liver parasite burden was measured by quantification of parasite-specific 18S rRNA in total liver RNA by quantitative-competitive reverse transcription-PCR and by an automated 5' exonuclease PCR. Sporozoite-challenged TCRdelta(-/-) mice showed a significant (P < 0.01) increase in liver parasite burden compared to similarly challenged immunocompetent mice. In support of this result, TCRdelta(-/-) mice were also found to be more susceptible than immunocompetent mice to a sporozoite challenge when blood-stage parasitemia was used as a readout. A greater percentage of TCRdelta(-/-) mice than of immunocompetent mice progressed to a blood-stage infection when challenged with five or fewer sporozoites (odds ratio = 2.35, P = 0.06). TCRdelta(-/-) mice receiving a single irr-spz immunization showed percent inhibition of liver parasites comparable to that of immunized immunocompetent mice following a sporozoite challenge. These data support the hypothesis that gammadelta T cells are a component of early immunity directed against malaria preerythrocytic parasites and suggest that gammadelta T cells are not required for the induction of an effector alphabeta T-cell immune response generated by irr-spz immunization.
Figures
References
-
- Briones M R S, Tsuji M, Nussenzweig V. The large difference in infectivity for mice of Plasmodium berghei and Plasmodium yoelii sporozoites can not be correlated with their ability to enter hepatocytes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1996;77:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Clyde D F, McCarthy V C, Miller R M, Hornick R B. Specificity of protection of man immunized against sporozoite induced falciparum malaria. Am J Med Sci. 1973;266:398–403. - PubMed
-
- Clyde D F, Most H, McCarthy V C, Vanderberg J P. Immunization of man against sporozoite-induced falciparum malaria. Am J Med Sci. 1973;266:169–177. - PubMed
-
- Doolan D L, Hoffman S L. Multi-gene vaccination against malaria: a multistage, multi-immune response approach. Parasitol Today. 1997;13:171–178. - PubMed
-
- Edelman R, Hoffman S L, Davis J R, Beier M, Sztein M B, Lesonsky G, Herrington D A, Eddy H A, Hollingdale M R, Gordon D M, Clyde D F. Long-term persistence of sterile immunity in a volunteer immunized with X-irradiated Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites. J Infect Dis. 1993;168:1066–1070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

