Respiratory actions of tachykinins in the nucleus of the solitary tract: characterization of receptors using selective agonists and antagonists
- PMID: 10725260
- PMCID: PMC1571949
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703172
Respiratory actions of tachykinins in the nucleus of the solitary tract: characterization of receptors using selective agonists and antagonists
Abstract
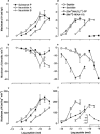
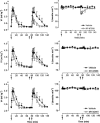
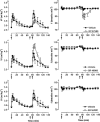
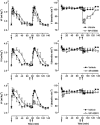
1. The respiratory response to microinjection of tachykinins and analogues into the commissural nucleus of the solitary tract (cNTS) of urethane-anaesthetized rats was investigated in the presence and absence of selective tachykinin NK(1), NK(2) and NK(3) antagonists (RP 67580, SR 48968 and SR 142801, respectively). 2. All tachykinins, except for the selective NK(2) agonist, [Nle(10)]-NKA(4-10), increased tidal volume (VT). The rank potency order of naturally-occurring tachykinins was neurokinin A (NKA)> or =substance P (SP)>>NKB, whereas the rank order for selective analogues was senktide> or = septide>> [Sar(9),Met(O(2))(11)]-SP>>[Nle(10)]-NKA(4-10). Septide (NK(1)-selective) and senktide (NK(3)-selective) were 22 fold more potent (pD(2) approximately 12) at stimulating VT than SP (pD(2) approximately 10.5). 3. Tachykinin agonists produced varying degrees of respiratory slowing, independent of changes in VT. At doses producing maximum stimulation of VT, agonists induced either a mild (<10 breaths min(-1) decrease; SP and septide), moderate (10 - 25 breaths min(-1) decrease; NKA, NKB and [Sar(9),Met(O(2)]-SP) or severe ( approximately 40 breaths min(-1) decrease; senktide) bradypnoea. [Nle(10)]-NKA(4-10) produced a dose-dependent bradypnoea without affecting VT. 4. RP 67580 significantly attenuated the VT response to SP (33 pmol) and NKA (10 pmol) but not NKB (100 pmol). In the presence of RP 67580, the mild bradypnoeic response to NKB was significantly enhanced whereas SP and NKA induced a bradyapnea which was not observed in the absence of RP 67580. SR 48968 had no effect on the VT response to SP or NKB, markedly enhanced the VT response to NKA and completely blocked the bradypnoeic response to [Nle(10)]-NKA(4-10). Only SR142801 attenuated the VT response to NKB. 5. The present data suggest that all three tachykinin receptors (NK(1), NK(2) and NK(3)) are present in the cNTS and are involved in the central control of respiration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Respiratory actions of tachykinins in the nucleus of the solitary tract: effect of neonatal capsaicin pretreatment.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Mar;129(6):1132-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703173. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10725261 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular and behavioural effects of centrally administered tachykinins in the rat: characterization of receptors with selective antagonists.Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):240-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13058.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7518304 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of selective tachykinin-receptor antagonists on tachykinin-induced airway mucus secretion in the rat.Neuropeptides. 1999 Feb;33(1):55-61. doi: 10.1054/npep.1999.0014. Neuropeptides. 1999. PMID: 10657472
-
Selective agonists of tachykinin binding sites.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1990;4(3):257-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1990.tb00493.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1990. PMID: 2165464 Review.
-
Tachykinin NK2 antagonist for treatments of various disease states.Auton Neurosci. 2021 Nov;235:102865. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2021.102865. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Auton Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34358844 Review.
Cited by
-
Ventilatory effects of substance P-saporin lesions in the nucleus tractus solitarii of chronically hypoxic rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Aug;301(2):R343-50. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00375.2010. Epub 2011 May 18. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21593425 Free PMC article.
-
Substance P - a regulatory peptide with defense and repair functions. Results and perspectives for the fight against COVID-19.Front Neurol. 2024 May 30;15:1370454. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1370454. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38872816 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identity, anatomy, gene expression and function of neural crest vs. placode-derived nociceptors in the lower airways.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Jan 18;742:135505. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135505. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33197519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective G protein signaling driven by substance P-neurokinin receptor dynamics.Nat Chem Biol. 2022 Jan;18(1):109-115. doi: 10.1038/s41589-021-00890-8. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Nat Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 34711980 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-induced plasticity of the afferent innervation of the airways.Environ Health Perspect. 2001 Aug;109 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):567-71. doi: 10.1289/ehp.01109s4567. Environ Health Perspect. 2001. PMID: 11544165 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BAILEY C.P., JONES R.S.G. NK2-receptor activation increases spontaneous GABA-release in the rat nucleus tractus solitarius in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999;127:48P.
-
- CAMMACK C., LOGAN S.D. Excitation of rat sympathetic preganglionic neurones by selective activation of the NK1 receptor. J. Autonom. Nerv. Sys. 1996;57:87–92. - PubMed
-
- CARPENTIER C., BAUDE A. Immunocytochemical localisation of NK3 receptors in the dorsal vagal complex of rat. Brain Res. 1996;734:327–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

