beta-arrestin-dependent endocytosis of proteinase-activated receptor 2 is required for intracellular targeting of activated ERK1/2
- PMID: 10725339
- PMCID: PMC2174299
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.148.6.1267
beta-arrestin-dependent endocytosis of proteinase-activated receptor 2 is required for intracellular targeting of activated ERK1/2
Abstract
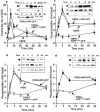
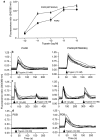
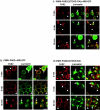
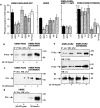
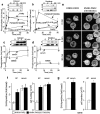
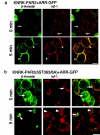
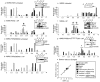
Recently, a requirement for beta-arrestin-mediated endocytosis in the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) by several G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) has been proposed. However, the importance of this requirement for function of ERK1/2 is unknown. We report that agonists of Galphaq-coupled proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) stimulate formation of a multiprotein signaling complex, as detected by gel filtration, immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence. The complex, which contains internalized receptor, beta-arrestin, raf-1, and activated ERK, is required for ERK1/2 activation. However, ERK1/2 activity is retained in the cytosol and neither translocates to the nucleus nor causes proliferation. In contrast, a mutant PAR2 (PAR2deltaST363/6A), which is unable to interact with beta-arrestin and, thus, does not desensitize or internalize, activates ERK1/2 by a distinct pathway, and fails to promote both complex formation and cytosolic retention of the activated ERK1/2. Whereas wild-type PAR2 activates ERK1/2 by a PKC-dependent and probably a ras-independent pathway, PAR2(deltaST363/6A) appears to activate ERK1/2 by a ras-dependent pathway, resulting in increased cell proliferation. Thus, formation of a signaling complex comprising PAR2, beta-arrestin, raf-1, and activated ERK1/2 might ensure appropriate subcellular localization of PAR2-mediated ERK activity, and thereby determine the mitogenic potential of receptor agonists.
Figures

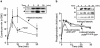


References
-
- Böhm S.K., Khitin L., Smeekens S.P., Grady E.F., Payan D.G., Bunnett N.W. Identification of potential tyrosine-containing endocytic motifs in the carboxyl-tail and seventh transmembrane domain of the neurokinin 1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:2363–2372. - PubMed
-
- Böhm S.K., Khitin L.M., Grady E.F., Aponte G., Payan D.G., Bunnett N.W. Mechanisms of desensitization and resensitization of proteinase-activated receptor-2. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:22003–22016. - PubMed
-
- Bornfeldt K.E., Campbell J.S., Koyama H., Argast G.M., Leslie C.C., Raines E.W., Krebs E.G., Ross R. The mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway can mediate growth inhibition and proliferation in smooth muscle cells. Dependence on the availability of downstream targets. J. Clin. Invest. 1997;100:875–885. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

