Light stress-regulated two-helix proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana related to the chlorophyll a/b-binding gene family
- PMID: 10725357
- PMCID: PMC16310
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.7.3741
Light stress-regulated two-helix proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana related to the chlorophyll a/b-binding gene family
Abstract
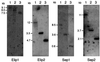
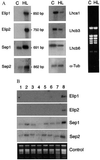
The chlorophyll a/b, chlorophyll a/c, and chlorophyll a/a light-harvesting proteins are part of an extended gene family that also includes the transiently expressed stress proteins, the Elips (early light-induced proteins). Four Elip homologue proteins, encoded by single-copy nuclear genes, have been identified in the Arabidopsis thaliana database. These proteins were divided into two groups according to the expression pattern under light-stress conditions and the predicted secondary structure. Group one included two members of the Elip family with three predicted transmembrane helices and a gene expression strictly related to light stress. Group two included two proteins, the Seps (stress-enhanced proteins), which possessed two predicted transmembrane segments. The transcripts of Sep1 and Sep2 were present under low light conditions, but their level increased 4- to 10-fold during illumination of plants with high-intensity light. Preliminary data indicated that the induced transcripts were translated in vivo. Other physiological stress conditions, such as cold, heat, desiccation, salt, wounding, or oxidative stress, did not significantly influence the expression of Sep genes. In vitro import of radioactively labeled precursors of Seps into isolated chloroplasts confirmed the thylakoid membrane localization of these proteins. Considering the predicted protein structure and homology to other pigment-antenna proteins, the two-helix Seps might represent an evolutionary missing link between the one- and three-helix antenna proteins present in pro- and eukaryota.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Light stress-induced one-helix protein of the chlorophyll a/b-binding family associated with photosystem I.Plant Physiol. 2003 Jun;132(2):811-20. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.019281. Epub 2003 May 15. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12805611 Free PMC article.
-
A cyanobacterial gene family coding for single-helix proteins resembling part of the light-harvesting proteins from higher plants.Biochemistry. 1999 Jul 20;38(29):9397-404. doi: 10.1021/bi990545+. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10413515
-
An Arabidopsis thaliana protein homologous to cyanobacterial high-light-inducible proteins.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Jan;42(2):345-51. doi: 10.1023/a:1006365213954. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10794534
-
Transiently expressed early light-inducible thylakoid proteins share transmembrane domains with light-harvesting chlorophyll binding proteins.Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Nov;13(5):583-93. doi: 10.1007/BF00027318. Plant Mol Biol. 1989. PMID: 2491675
-
Chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins: an extended family.Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 May;16(5):181-6. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90072-4. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991. PMID: 1882419 Review.
Cited by
-
LHC-like Proteins: The Guardians of Photosynthesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 28;24(3):2503. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032503. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional diversification of the light-harvesting complexes in photosynthetic eukaryotes.Photosynth Res. 2010 Nov;106(1-2):57-71. doi: 10.1007/s11120-010-9576-2. Epub 2010 Jul 2. Photosynth Res. 2010. PMID: 20596891 Review.
-
Comparative genomics and transcriptomics analysis reveals evolution patterns of selection in the Salix phylogeny.BMC Genomics. 2019 Mar 29;20(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5627-z. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30925896 Free PMC article.
-
The high light-inducible polypeptides stabilize trimeric photosystem I complex under high light conditions in Synechocystis PCC 6803.Plant Physiol. 2008 Jul;147(3):1239-50. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.121087. Epub 2008 May 23. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18502976 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analyses reveal two distinct transcriptional modules associated with pollen shedding time in pine.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jul 22;21(1):504. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06880-9. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32698817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolfe R G, Cunningham F X, Durnford D, Green B R, Gantt E. Nature (London) 1994;367:566–568.
-
- Durnford D G, Deane J A, Tan S, McFadden G I, Gantt E, Green B R. J Mol Evol. 1999;48:59–68. - PubMed
-
- Jansson S. Trends Plant Sci. 1999;4:236–240. - PubMed
-
- Funk C, Schröder W, Napiwotzki A, Tjus S, Renger G, Andersson B. Biochemistry. 1995;34:11133–11141. - PubMed
-
- Kim S, Sandusky P, Bowlby N R, Aebersold R, Green B R, Vlahakis S, Yokum C F, Pichersky E. FEBS Lett. 1992;314:67–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

