Accuracy of thymine-thymine dimer bypass by Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA polymerase eta
- PMID: 10725365
- PMCID: PMC16198
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.7.3094
Accuracy of thymine-thymine dimer bypass by Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA polymerase eta
Abstract
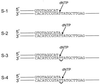
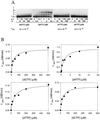
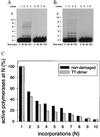
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD30 gene functions in error-free replication of UV-damaged DNA. RAD30 encodes a DNA polymerase, Pol eta, which inserts two adenines opposite the two thymines of a cis-syn thymine-thymine (T-T) dimer. Here we use steady-state kinetics to determine the accuracy of DNA synthesis opposite the T-T dimer. Surprisingly, the accuracy of DNA synthesis opposite the damaged DNA is nearly indistinguishable from that opposite nondamaged DNA, with frequencies of misincorporation of about 10(-2) to 10(-3). These studies support the hypothesis that unlike most DNA polymerases, Pol eta is able to tolerate distortions in DNA resulting from damage, which then enables the polymerase to utilize the intrinsic base pairing ability of the T-T dimer.
Figures


Comment in
-
The many faces of DNA polymerases: strategies for mutagenesis and for mutational avoidance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 May 23;97(11):5681-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.120152397. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10811923 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

