The neuregulin receptor ErbB-4 interacts with PDZ-containing proteins at neuronal synapses
- PMID: 10725395
- PMCID: PMC16285
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.7.3596
The neuregulin receptor ErbB-4 interacts with PDZ-containing proteins at neuronal synapses
Abstract
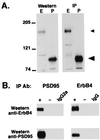
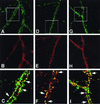
Neuregulins regulate the expression of ligand- and voltage-gated channels in neurons and skeletal muscle by the activation of their cognate tyrosine kinase receptors, ErbB 1-4. The subcellular distribution and mechanisms that regulate the localization of ErbB receptors are unknown. We have found that ErbB receptors are present in brain subcellular fractions enriched for postsynaptic densities (PSD). The ErbB-4 receptor is unique among the ErbB proteins because its C-terminal tail (T-V-V) conforms to a sequence that binds to a protein motif known as the PDZ domain. Using the yeast two-hybrid system, we found that the C-terminal region of ErbB-4 interacts with the three related membrane-associated guanylate kinases (MAGUKs) PSD-95/SAP90, PSD-93/chapsyn-110, and SAP 102, which harbor three PDZ domains, as well as with beta(2)-syntrophin, which has a single PDZ domain. As with N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, ErbB4 interacts with the first two PDZ domains of PSD-95. Using coimmunoprecipitation assays, we confirmed the direct interactions between ErbB-4 and PSD-95 in transfected heterologous cells, as well as in vivo, where both proteins are coimmunoprecipitated from brain lysates. Moreover, evidence for colocalization of these proteins was also observed by immunofluorescence in cultured hippocampal neurons. ErbB-4 colocalizes with PSD-95 and NMDA receptors at a subset of excitatory synapses apposed to synaptophysin-positive presynaptic terminals. The capacity of ErbB receptors to interact with PDZ-domain proteins at cell junctions is conserved from invertebrates to mammals. As discussed, the interactions found between receptor tyrosine kinases and MAGUKs at neuronal synapses may have important implications for activity-dependent plasticity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CRIPT, a novel postsynaptic protein that binds to the third PDZ domain of PSD-95/SAP90.Neuron. 1998 Apr;20(4):693-707. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)81009-0. Neuron. 1998. PMID: 9581762
-
SAPAPs. A family of PSD-95/SAP90-associated proteins localized at postsynaptic density.J Biol Chem. 1997 May 2;272(18):11943-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.18.11943. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9115257
-
Erbin is a protein concentrated at postsynaptic membranes that interacts with PSD-95.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 1;276(22):19318-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100494200. Epub 2001 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11279080
-
PSD-95-like membrane associated guanylate kinases (PSD-MAGUKs) and synaptic plasticity.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011 Apr;21(2):306-12. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2011.03.001. Epub 2011 Mar 28. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21450454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of postsynaptic density-95/synapse-associated protein 90 and its interacting proteins in the organization of synapses.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999 Oct 30;56(5-6):461-72. doi: 10.1007/s000180050445. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999. PMID: 11212298 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The human PDZome: a gateway to PSD95-Disc large-zonula occludens (PDZ)-mediated functions.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Sep;12(9):2587-603. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O112.021022. Epub 2013 May 30. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23722234 Free PMC article.
-
Neuregulin 1 expression and electrophysiological abnormalities in the Neuregulin 1 transmembrane domain heterozygous mutant mouse.PLoS One. 2015 May 19;10(5):e0124114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124114. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25992564 Free PMC article.
-
Neuregulin1 (NRG1) signaling through Fyn modulates NMDA receptor phosphorylation: differential synaptic function in NRG1+/- knock-outs compared with wild-type mice.J Neurosci. 2007 Apr 25;27(17):4519-29. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4314-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17460065 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic labeling reveals novel cellular targets of schizophrenia susceptibility gene: distribution of GABA and non-GABA ErbB4-positive cells in adult mouse brain.J Neurosci. 2014 Oct 1;34(40):13549-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2021-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25274830 Free PMC article.
-
Update on HER-2 as a target for cancer therapy: intracellular signaling pathways of ErbB2/HER-2 and family members.Breast Cancer Res. 2001;3(6):385-9. doi: 10.1186/bcr327. Epub 2001 Oct 4. Breast Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11737890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fischbach G D, Rosen K M. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1997;20:429–458. - PubMed
-
- Zhang D, Frantz G, Godowski P J. Mol Psychiatry. 1998;2:112–115. - PubMed
-
- Lemke G. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996;7:247–262. - PubMed
-
- Burden S, Yarden Y. Neuron. 1997;18:847–855. - PubMed
-
- Morris J K, Lin W, Hauser C, Marchuk Y, Getman D, Lee K F. Neuron. 1999;23:273–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

