Gene transfer of the neuronal NO synthase isoform to cirrhotic rat liver ameliorates portal hypertension
- PMID: 10727442
- PMCID: PMC377460
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI7997
Gene transfer of the neuronal NO synthase isoform to cirrhotic rat liver ameliorates portal hypertension
Abstract
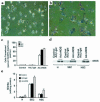
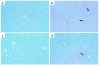
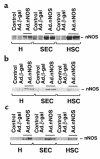
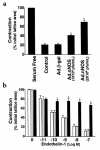
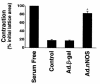
Reduced production of nitric oxide (NO) in the cirrhotic liver results from a defect in hepatic endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase (ecNOS) and appears to contribute to the high intrahepatic resistance and portal hypertension typical of cirrhosis. Therefore, we postulated that targeting a heterologous NOS isoform to sinusoidal endothelial cells or other perisinusoidal cells, such as hepatic stellate cells, would counter the defect in NO production and reduce resistance to blood flow. Recombinant adenovirus (Ad) carrying the neuronal NOS gene (nNOS) targeted liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, stellate cells, and hepatocytes more efficiently than the corresponding cells in cirrhotic livers, but transduction rates were substantial even in cirrhotic animals. Expression of nNOS in each liver cell type, whether from normal or injured liver, caused increased NO production and inhibited endothelin-1-induced contractility of perisinusoidal stellate cells. Finally, in 2 different in vivo models of cirrhosis and portal hypertension, transduction of livers with recombinant Ad.nNOS significantly reduced intrahepatic resistance and portal pressure. The data highlight the feasibility of gene transfer to diseased liver and hepatic cells and demonstrate the potential of a novel therapy for portal hypertension caused by cirrhosis.
Figures
References
-
- Friedman SL. Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. Mechanisms and treatment strategies. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1828–1835. - PubMed
-
- Shah V, Garcia-Cardena G, Sessa WC, Groszmann RJ. The hepatic circulation in health and disease: report of a single-topic symposium. Hepatology. 1998;27:279–288. - PubMed
-
- Bauer M, Zhang JX, Bauer I, Clemens MG. ET-1 induced alterations of hepatic microcirculation: sinusoidal and extrasinusoidal sites of action. Am J Physiol. 1994;267:G143–G149. - PubMed
-
- Zhang JX, Pegoli WJ, Clemens MG. Endothelin-1 induces direct constriction of hepatic sinusoids. Am J Physiol. 1994;266:G624–G632. - PubMed
-
- Bauer M, et al. Chronic ethanol consumption increases hepatic sinusoidal contractile response to endothelin-1 in the rat. Hepatology. 1995;22:1565–1576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

