NP and L proteins of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) are sufficient for efficient transcription and replication of LCMV genomic RNA analogs
- PMID: 10729120
- PMCID: PMC111854
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.8.3470-3477.2000
NP and L proteins of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) are sufficient for efficient transcription and replication of LCMV genomic RNA analogs
Abstract
The genome of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) consists of two negative-sense single-stranded RNA segments, designated L and S. Both segments contain two viral genes in an ambisense coding strategy, with the genes being separated by an intergenic region (IGR). We have developed a reverse genetic system that allows the investigation of cis-acting signals and trans-acting factors involved in transcription and replication of LCMV. To this end, we constructed an LCMV S minigenome consisting of a negative-sense copy of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter gene flanked upstream by the S 5' untranslated region (UTR) and IGR and downstream by the S 3' UTR. CAT expression was detected in LCMV-infected cells transfected with the minigenome RNA. Intracellular coexpression of the LCMV minigenome and LCMV L and NP proteins supplied from cotransfected plasmids driven by the T7 RNA polymerase provided by the recombinant vaccinia virus vTF7-3 resulted in high levels of CAT activity and synthesis of subgenomic CAT mRNA and antiminigenome RNA species. Thus, L and NP represent the minimal viral trans-acting factors required for efficient RNA synthesis mediated by LCMV polymerase.
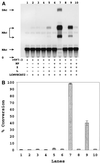
Figures

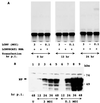
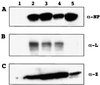

References
-
- Auperin D D, Compans R W, Bishop D H. Nucleotide sequence conservation at the 3′ termini of the virion RNA species of New World and Old World arenaviruses. Virology. 1982;121:200–203. - PubMed
-
- Auperin D D, Sasso D R, McCormick J B. Nucleotide sequence of the glycoprotein gene and intergenic region of the Lassa virus S genome RNA. Virology. 1986;154:155–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

