Drug resistant tuberculosis can be controlled, says WHO
- PMID: 10731157
- PMCID: PMC1127184
Drug resistant tuberculosis can be controlled, says WHO
Abstract
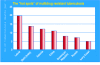
PIP: Hard evidence on the prevention of drug resistant tuberculosis by using properly controlled treatment programs was gathered by the WHO. However, the WHO warned that a window of opportunity to prevent the spread of drug resistant strains will be missed if urgent action is not taken to persuade more health authorities to use its recommended treatment strategy. Reports from 58 countries have shown a disturbingly high prevalence of drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Eastern Europe and Asia, while countries that have used the recommended treatment strategy tend to have low rates of resistance. The WHO has been arguing for directly observed treatment, short course for years on the basis of small-scale studies that show it helps to prevent the emergence of resistance. In countries like India, China, Indonesia, Bangladesh, and Pakistan, the scale of drug resistance is still unknown with high incidence of tuberculosis. Prevalence of tuberculosis is still high in Estonia, as well as in some provinces of India and China although the scale of the problem is small.
Figures
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources