Essential function of Wnt-4 in mammary gland development downstream of progesterone signaling
- PMID: 10733525
- PMCID: PMC316462
Essential function of Wnt-4 in mammary gland development downstream of progesterone signaling
Abstract
Female reproductive hormones control mammary gland morphogenesis. In the absence of the progesterone receptor (PR) from the mammary epithelium, ductal side-branching fails to occur. We can overcome this defect by ectopic expression of the protooncogene Wnt-1. Transplantation of mammary epithelia from Wnt-4(-)/(-) mice shows that Wnt-4 has an essential role in side-branching early in pregnancy. PR and Wnt-4 mRNAs colocalize to the luminal compartment of the ductal epithelium. Progesterone induces Wnt-4 in mammary epithelial cells and is required for increased Wnt-4 expression during pregnancy. Thus, Wnt signaling is essential in mediating progesterone function during mammary gland morphogenesis.
Figures
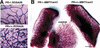
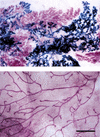
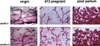
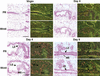

References
-
- Bjornson C, Rietze R, Reynolds B, Magli M, Vescovi A. Turning brain into blood: A hematopoietic fate adopted by adult neural stem cells in vivo. Science. 1999;283:534–537. - PubMed
-
- Bocchinfuso W, Hively W, Couse J, Varmus H, Korach K. A mouse mammary tumor virus-Wnt-1 transgene induces mammary gland hyperplasia and tumorigenesis in mice lacking estrogen receptor-alpha. Cancer Res. 1999;59:1869–1876. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury JM, Edwards PA, Niemeyer CC, Dale TC. Wnt-4 expression induces a pregnancy-like growth pattern in reconstituted mammary glands in virgin mice. Dev Biol. 1995;170:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Cadigan K, Nusse R. Wnt signaling: A common theme in animal development. Genes & Dev. 1997;11:3286–3305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
