PERP, an apoptosis-associated target of p53, is a novel member of the PMP-22/gas3 family
- PMID: 10733530
- PMCID: PMC316461
PERP, an apoptosis-associated target of p53, is a novel member of the PMP-22/gas3 family
Erratum in
- Genes Dev 2000 Jul 15;14(14):1835
Abstract
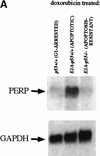
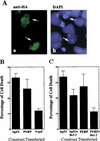
The p53 tumor suppressor activates either cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in response to cellular stress. Mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) provide a powerful primary cell system to study both p53-dependent pathways. Specifically, in response to DNA damage, MEFs undergo p53-dependent G(1) arrest, whereas MEFs expressing the adenovirus E1A oncoprotein undergo p53-dependent apoptosis. As the p53-dependent apoptosis pathway is not well understood, we sought to identify apoptosis-specific p53 target genes using a subtractive cloning strategy. Here, we describe the characterization of a gene identified in this screen, PERP, which is expressed in a p53-dependent manner and at high levels in apoptotic cells compared with G(1)-arrested cells. PERP induction is linked to p53-dependent apoptosis, including in response to E2F-1-driven hyperproliferation. Furthermore, analysis of the PERP promoter suggests that PERP is directly activated by p53. PERP shows sequence similarity to the PMP-22/gas3 tetraspan membrane protein implicated in hereditary human neuropathies such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth. Like PMP-22/gas3, PERP is a plasma membrane protein, and importantly, its expression causes cell death in fibroblasts. Taken together, these data suggest that PERP is a novel effector of p53-dependent apoptosis.
Figures










References
-
- Bates S, Phillips AC, Clark PA, Stott F, Peters G, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH. p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature. 1998;395:124–125. - PubMed
-
- Brugarolas J, Chandrasekaran C, Gordon JI, Beach D, Jacks T, Hannon GH. Radiation-induced cell cycle arrest compromised by p21 deficiency. Nature. 1995;377:552–557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
