A two-component multidrug efflux pump, EbrAB, in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 10735876
- PMCID: PMC111282
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.8.2307-2310.2000
A two-component multidrug efflux pump, EbrAB, in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
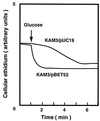
Genes (ebrAB) responsible for ethidium resistance were cloned from chromosomal DNA of Bacillus subtilis ATCC 9372. The recombinant plasmid produced elevated resistance against ethidium bromide, acriflavine, pyronine Y, and safranin O not only in Escherichia coli but also in B. subtilis. It also caused an elevated energy-dependent efflux of ethidium in E. coli. EbrA and EbrB showed high sequence similarity with members of the small multidrug resistance (SMR) family of multidrug efflux pumps. Neither ebrA nor ebrB was sufficient for resistance, but introduction of the two genes carried on different plasmids conferred drug resistance. Thus, both EbrA and EbrB appear to be necessary for activity of the multidrug efflux pump. In known members of the SMR family, only one gene produces drug efflux. Thus, EbrAB is a novel SMR family multidrug efflux pump with two components.
Figures
References
-
- Bolhuis H, van Veen H W, Poolman B, Driessen A J, Konings W N. Mechanisms of multidrug transporters. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1997;21:55–84. - PubMed
-
- Cole S T. Nucleotide sequence and comparative analysis of the frd operon encoding the fumarate reductase of Proteus vulgaris. Extensive sequence divergence of the membrane anchors and absence of an frd-linked ampC cephalosporinase gene. Eur J Biochem. 1987;167:481–488. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg D, Schwarz E, Komaromy M, Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984;179:125–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

