A novel X-linked dominant condition: X-linked congenital isolated ptosis
- PMID: 10739771
- PMCID: PMC1288214
- DOI: 10.1086/302860
A novel X-linked dominant condition: X-linked congenital isolated ptosis
Abstract
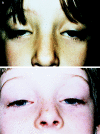
We present a large family with a previously undescribed condition: X-linked dominant congenital bilateral isolated ptosis. Linkage analysis defined a critical region between Xq24 and Xq27.1, with a maximum single-point LOD score of 2.88 at DXS1047 and DXS984. Male and female family members are equally affected, providing an example of an X-linked, truly dominant condition.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- The Genome Database, http://www.hgmp.mrc.ac.uk/gdb (for markers)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for 1p32-1p34.1 [MIM 178300], X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth [MIM 302800], hypophosphatemia [MIM 307800], and X-linked dominant chondroplasia punctata [MIM 302960])
References
-
- Cohen MA (1972) Congenital ptosis: a new pedigree and classification. Arch Ophthalmol 87:161–163 - PubMed
-
- Collins A, Teague J, Keats BJ, Morton NE (1996) Linkage map integration. Genomics 36:157–162 - PubMed
-
- O'Connell JR, Weeks DE (1995) The VITESSE algorithm for rapid exact multilocus linkage analysis via genotype set—recording and fuzzy inheritance. Nat Genet 11:402–408 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases