The role of lipopolysaccharide injected systemically in the reactivation of collagen-induced arthritis in mice
- PMID: 10742285
- PMCID: PMC1571961
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703166
The role of lipopolysaccharide injected systemically in the reactivation of collagen-induced arthritis in mice
Abstract
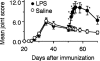
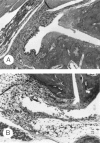
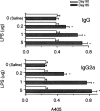
1. We investigated the role of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the reactivation of autoimmune disease by using collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice in which autoimmunity to the joint cartilage component type II collagen (CII) was involved. 2. CIA was induced by immunization with CII emulsified with complete Freund's adjuvant at the base of the tail (day 0) followed by a booster injection on day 21. Varying doses of LPS from E. coli were i.p. injected on day 50. 3. Arthritis began to develop on day 25 after immunization with CII and reached a peak on day 35. Thereafter, arthritis subsided gradually but moderate joint inflammation was still observed on day 50. An i.p. injection of LPS on day 50 markedly reactivated arthritis on a dose-related fashion. Histologically, on day 55, there were marked oedema of synovium which had proliferated by the day of LPS injection, new formation of fibrin, and intense infiltration of neutrophils accompanied with a large number of mononuclear cells. The reactivation of CIA by LPS was associated with increases in anti-CII IgG and IgG2a antibodies as well as various cytokines including IL-12, IFN-gamma, IL-1beta, and TNF-alpha. LPS from S. enteritidis, S. typhimurium, and K. neumoniae and its component, lipid A from E. coli also reactivated the disease. Polymyxin B sulphate suppressed LPS- or lipid A-induced reactivation of CIA. 4. These results suggest that LPS may play an important role in the reactivation of autoimmune joint inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis in humans.
Figures

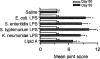


References
-
- AREND W.P., DAYER J.M. Inhibition of the production and effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in rheumatoid arthritis. Arth. Rheum. 1995;38:151–160. - PubMed
-
- BRENNAN F.M., MAINI R.N., FELDMANN M. TNF-alpha: a pivotal role in rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1992;31:293–298. - PubMed
-
- CLAQUE R.B., MOORE L.J. IgG and IgM antibody to native type II collagen in rheumatoid arthritis serum and synovial fluid: evidence for the presence of collagen-anticollagen immune complexes in synovial fluid. Arth. Rheum. 1984;27:1370–1377. - PubMed
-
- COURTENAY J.S., DALLMAN M.J., DAYAN A.D., MARTIN A., MOSEDALE B. Immunization against heterologous type II collagen induces arthritis in mice. Nature. 1980;283:666–668. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

