Quantitative galactomannan detection is superior to PCR in diagnosing and monitoring invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in an experimental rat model
- PMID: 10747121
- PMCID: PMC86459
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.4.1434-1438.2000
Quantitative galactomannan detection is superior to PCR in diagnosing and monitoring invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in an experimental rat model
Abstract
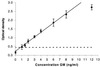
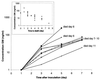
Two diagnostic tests, an Aspergillus-specific PCR and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the quantitative determination of galactomannan, were compared for diagnosing and monitoring invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Persistently neutropenic rats with left-sided invasive pulmonary aspergillosis were sacrificed at regular intervals after inoculation. Blood samples and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid were cultured and tested by PCR as well as by ELISA. Disseminated fungal infection in extrapulmonary organs was determined. The sensitivity of the ELISA was higher than that of the PCR on all days of measurements, in both blood and BAL fluid. Positive PCR or ELISA results in blood were not significantly associated with disseminated fungal infection. Serial testing in a separate group of rats showed consistently increasing concentrations of circulating galactomannan during the course of disease, while a positive PCR could be followed by negative results. The concentration of galactomannan was highly predictive for the time of survival (P < 0.0001). It was concluded that, in this model, quantitative galactomannan detection is superior to PCR in diagnosing and monitoring invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.
Figures
References
-
- Aisner J, Wiernik P H, Schimpff S C. Treatment of invasive aspergillosis: relation of early diagnosis and treatment to response. Ann Intern Med. 1977;86:539–543. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong D. Overview of invasive fungal infections and clinical presentation. In: Meunier F, et al., editors. Balliere's clinical infectious diseases. Vol. 2. London, United Kingdom: Balliere Tindal; 1995. pp. 17–24.
-
- Bretagne S, Costa J M, Bart-Delabesse E, Dhedin N, Rieux C, Cordonnier C. Comparison of serum galactomannan antigen detection and competitive polymerase chain reaction for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:1407–1412. - PubMed
-
- Crampin A C, Matthews R C. Application of the polymerase chain reaction to the diagnosis of candidosis by amplification of an HSP 90 gene fragment. J Med Microbiol. 1993;39:233–238. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

