Disruption of T cell homeostasis in mice expressing a T cell-specific dominant negative transforming growth factor beta II receptor
- PMID: 10748236
- PMCID: PMC2193176
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.191.7.1187
Disruption of T cell homeostasis in mice expressing a T cell-specific dominant negative transforming growth factor beta II receptor
Abstract
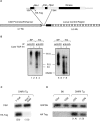
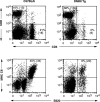
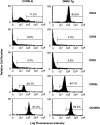
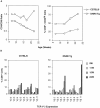
The immune system, despite its complexity, is maintained at a relative steady state. Mechanisms involved in maintaining lymphocyte homeostasis are poorly understood; however, recent availability of transgenic (Tg) and knockout mouse models with altered balance of lymphocyte cell populations suggest that cytokines play a major role in maintaining lymphocyte homeostasis. We show here that transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta plays a critical role in maintaining CD8(+) T cell homeostasis in a Tg mouse model that specifically overexpresses a dominant negative TGF-beta II receptor (DNRII) on T cells. DNRII T cell Tg mice develop a CD8(+) T cell lymphoproliferative disorder resulting in the massive expansion of the lymphoid organs. These CD8(+) T cells are phenotypically "naive" except for the upregulation of the cell surface molecule CD44, a molecule usually associated with memory T cells. Despite their dominance in the peripheral lymphoid organs, CD8(+) T cells appear to develop normally in the thymus, suggesting that TGF-beta exerts its homeostatic control in the peripheral immune system.
Figures

References
-
- Kingsley D.M. The TGF-β superfamilynew members, new receptors, and new genetic tests of function in different organisms. Genes Dev. 1994;8:133–146. - PubMed
-
- Letterio J.J., Roberts A.B. Transforming growth factor-beta1-deficient miceidentification of isoform-specific activities in vivo. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996;59:769–774. - PubMed
-
- Ruscetti F., Varesio L., Ochoa A., Ortaldo J. Pleiotropic effects of transforming growth factor-beta on cells of the immune system. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1993;685:488–500. - PubMed
-
- Gamble J.R., Khew-Goodall Y., Vadas M.A. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits E-selectin expression on human endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 1993;150:4494–4503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

