The Fn14 immediate-early response gene is induced during liver regeneration and highly expressed in both human and murine hepatocellular carcinomas
- PMID: 10751351
- PMCID: PMC1876890
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64996-6
The Fn14 immediate-early response gene is induced during liver regeneration and highly expressed in both human and murine hepatocellular carcinomas
Abstract
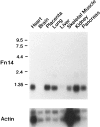
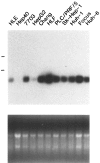
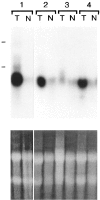
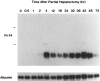
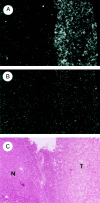
Polypeptide growth factors stimulate mammalian cell proliferation by binding to specific cell surface receptors. This interaction triggers numerous biochemical responses including the activation of protein phosphorylation cascades and the enhanced expression of specific genes. We have identified several fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-inducible genes in murine NIH 3T3 cells and recently reported that one of them, the FGF-inducible 14 (Fn14) immediate-early response gene, is predicted to encode a novel, cell surface-localized type Ia transmembrane protein. Here, we report that the human Fn14 homolog is located on chromosome 16p13.3 and encodes a 129-amino acid protein with approximately 82% sequence identity to the murine protein. The human Fn14 gene, like the murine Fn14 gene, is expressed at elevated levels after FGF, calf serum or phorbol ester treatment of fibroblasts in vitro and is expressed at relatively high levels in heart and kidney in vivo. We also report that the human Fn14 gene is expressed at relatively low levels in normal liver tissue but at high levels in liver cancer cell lines and in hepatocellular carcinoma specimens. Furthermore, the murine Fn14 gene is rapidly induced during liver regeneration in vivo and is expressed at high levels in the hepatocellular carcinoma nodules that develop in the c-myc/transforming growth factor-alpha-driven and the hepatitis B virus X protein-driven transgenic mouse models of hepatocarcinogenesis. These results indicate that Fn14 may play a role in hepatocyte growth control and liver neoplasia.
Figures



References
-
- Van der Geer P, Hunter T, Lindberg RA: Receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and their signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1994, 10:251-337 - PubMed
-
- Winkles JA: Serum-and polypeptide growth factor-inducible gene expression in mouse fibroblasts. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 1998, 58:41-78 - PubMed
-
- Iyer VR, Eisen MB, Ross DT, Schuler G, Moore T, Lee JCF, Trent JM, Staudt LM, Hudson J, Boguski MS, Lashkari D, Shalon D, Botstein D, Brown PO: The transcriptional program in the response of human fibroblasts to serum. Science 1999, 283:83-87 - PubMed
-
- Fambrough D, McClure K, Kazlauskas A, Lander ES: Diverse signaling pathways activated by growth factor receptors induce broadly overlapping, rather than independent, sets of genes. Cell 1999, 97:727-741 - PubMed
-
- Winkles JA, Donohue PJ, Hsu DKW, Guo Y, Alberts GF, Peifley KA: Identification of FGF-1-inducible genes by differential display. Gallo L eds. Cardiovascular Disease 2. 1995, :pp 109-120 Plenum Press, New York
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

