Akt/protein kinase B prevents injury-induced motoneuron death and accelerates axonal regeneration
- PMID: 10751440
- PMCID: PMC6772200
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-08-02875.2000
Akt/protein kinase B prevents injury-induced motoneuron death and accelerates axonal regeneration
Abstract
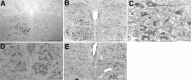
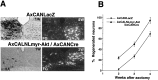
Motoneurons require neurotrophic factors for their survival and axonal projection during development, as well as nerve regeneration. By using the axotomy-induced neuronal death paradigm and adenovirus-mediated gene transfer, we attempted to gain insight into the functional significances of major growth factor receptor downstream cascades, Ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Ras-ERK) pathway and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-Akt (PI3K-Akt) pathway. After neonatal hypoglossal nerve transection, the constitutively active Akt-overexpressing neurons could survive as well as those overexpressing Bcl-2, whereas the constitutively active ERK kinase (MEK)-overexpressing ones failed to survive. A dominant negative Akt experiment demonstrated that inhibition of Akt pathway hastened axotomy-induced neuronal death in the neonate. In addition, the dominant active Akt-overexpressing adult hypoglossal neurons showed accelerated axonal regeneration after axotomy. These results suggest that Akt plays dual roles in motoneuronal survival and nerve regeneration in vivo and that PI3K-Akt pathway is probably more vital in neuronal survival after injury than Ras-ERK pathway.
Figures





References
-
- Akli S, Caillaud C, Vigne E, Stratford-Perricaudet LD, Poenaru L, Perricaudet M, Kahn A, Peschanski MR. Transfer of a foreign gene into the brain using adenovirus vectors. Nat Genet. 1993;3:224–228. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann A, Agapite J, McCall K, Steller H. The Drosophila gene hid is a direct molecular target of Ras-dependent survival signaling. Cell. 1998;95:331–341. - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 1999;96:857–868. - PubMed
-
- Burgering BM, Coffer PJ. Protein kinase B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction. Nature. 1995;376:599–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
