Molecular separation of two behavioral phenotypes by a mutation affecting the promoters of a Ca-activated K channel
- PMID: 10751451
- PMCID: PMC6772212
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-08-02988.2000
Molecular separation of two behavioral phenotypes by a mutation affecting the promoters of a Ca-activated K channel
Abstract
The Drosophila slowpoke gene encodes a BK-type calcium-activated potassium channel. Null mutations in slowpoke perturb the signaling properties of neurons and muscles and cause behavioral defects. The animals fly very poorly compared with wild-type strains and, after exposure to a bright but cool light or a heat pulse, exhibit a "sticky-feet" phenotype. Expression of slowpoke arises from five transcriptional promoters that express the gene in neural, muscle, and epithelial tissues. A chromosomal deletion (ash2(18)) has been identified that removes the neuronal promoters but not the muscle-tracheal cell promoter. This deletion complements the flight defect of slowpoke null mutants but not the sticky-feet phenotype. Electrophysiological assays confirm that the ash2(18) chromosome restores normal electrical properties to the flight muscle. This suggests that the flight defect arises from a lack of slowpoke expression in muscle, whereas the sticky-feet phenotype arises from a lack of expression in nervous tissue.
Figures
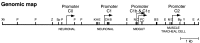




References
-
- Adelman JP, Shen KZ, Kavanaugh MP, Warren RA, Wu YN, Lagrutta A, Bond CT, North RA. Calcium-activated potassium channels expressed from cloned complementary DNAs. Neuron. 1992;9:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson NS, Robertson GA, Ganetzky B. A component of calcium-activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science. 1991;253:551–555. - PubMed
-
- Baumann A, Krah-Jentgens I, Müller R, Müller-Holtkamp F, Seidel R, Kecskemethy N, Casal J, Ferrus A, Pongs O. Molecular organization of the maternal effect region of the Shaker complex of Drosophila: characterization of an IA channel transcript with homology to vertebrate Na+ channel. EMBO J. 1987;6:3419–3429. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
