Links between replication, recombination and genome instability in eukaryotes
- PMID: 10754554
- PMCID: PMC3635104
- DOI: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)01568-1
Links between replication, recombination and genome instability in eukaryotes
Abstract
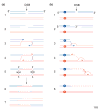
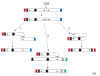
Double-strand breaks in DNA can be repaired by homologous recombination including break-induced replication. In this reaction, the end of a broken DNA invades an intact chromosome and primes DNA replication resulting in the synthesis of an intact chromosome. Break-induced replication has also been suggested to cause different types of genome rearrangements.
Figures

References
-
- Lett JT. Damage to DNA and chromatin structure from ionizing radiations, and the radiation sensitivities of mammalian cells. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1990;39:305–352. - PubMed
-
- Seigneur M, et al. RuvAB acts at arrested replication forks. Cell. 1998;30:419–430. - PubMed
-
- Haber JE. Meiosis: avoiding inappropriate relationships. Curr Biol. 1998;19:832–835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

