Identification and characterization of a novel serine-arginine-rich splicing regulatory protein
- PMID: 10757789
- PMCID: PMC85584
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.9.3049-3057.2000
Identification and characterization of a novel serine-arginine-rich splicing regulatory protein
Abstract
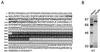
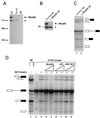
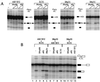
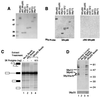
We have identified an 86-kDa protein containing a single amino-terminal RNA recognition motif and two carboxy-terminal domains rich in serine-arginine (SR) dipeptides. Despite structural similarity to members of the SR protein family, p86 is clearly unique. It is not found in standard SR protein preparations, does not precipitate in the presence of high magnesium concentrations, is not recognized by antibodies specific for SR proteins, and cannot complement splicing-defective S100 extracts. However, we have found that p86 can inhibit the ability of purified SR proteins to activate splicing in S100 extracts and can even inhibit the in vitro and in vivo activation of specific splice sites by a subset of SR proteins, including ASF/SF2, SC35, and SRp55. In contrast, p86 activates splicing in the presence of SRp20. Thus, it appears that pairwise combination of p86 with specific SR proteins leads to altered splicing efficiency and differential splice site selection. In all cases, such regulation requires the presence of the two RS domains and a unique intervening EK-rich region, which appear to mediate direct protein-protein contact between these family members. Full-length p86, but not a mutant lacking the RS-EK-RS domains, was found to preferentially interact with itself, SRp20, ASF/SF2, SRp55, and, to a slightly lesser extent, SC35. Because of the primary sequence and unique properties of p86, we have named this protein SRrp86 for SR-related protein of 86 kDa.
Figures


References
-
- Abovich N, Rosbash M. Cross-intron bridging interactions in the yeast commitment complex are conserved in mammals. Cell. 1997;89:403–412. - PubMed
-
- Amrein H, Hedley M L, Maniatis T. The role of specific protein-RNA and protein-protein interactions in positive and negative control of pre-mRNA splicing by transformer-2. Cell. 1994;76:735–746. - PubMed
-
- Berget S M. Exon recognition in vertebrate splicing. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:2411–2414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
