HIV-1 gp120 and chemokines activate ion channels in primary macrophages through CCR5 and CXCR4 stimulation
- PMID: 10758170
- PMCID: PMC18318
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.090521697
HIV-1 gp120 and chemokines activate ion channels in primary macrophages through CCR5 and CXCR4 stimulation
Abstract
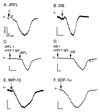
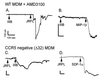
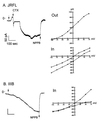
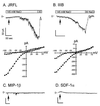
HIV type 1 (HIV-1) uses the chemokine receptors CCR5 and CXCR4 as coreceptors for entry into target cells. Here we show that the HIV-1 envelope gp120 (Env) activates multiple ionic signaling responses in primary human macrophages, which are important targets for HIV-1 in vivo. Env from both CCR5-dependent JRFL (R5) and CXCR4-dependent IIIB (X4) HIV-1 opened calcium-activated potassium (K(Ca)), chloride, and calcium-permeant nonselective cation channels in macrophages. These signals were mediated by CCR5 and CXCR4 because macrophages lacking CCR5 failed to respond to JRFL and an inhibitor of CXCR4 blocked ion current activation by IIIB. MIP-1beta and SDF-1alpha, chemokine ligands for CCR5 and CXCR4, respectively, also activated K(Ca) and Cl(-) currents in macrophages, but nonselective cation channel activation was unique to gp120. Intracellular Ca(2+) levels were also elevated by gp120. The patterns of activation mediated by CCR5 and CXCR4 were qualitatively similar but quantitatively distinct, as R5 Env activated the K(Ca) current more frequently, elicited Cl(-) currents that were approximately 2-fold greater in amplitude, and elevated intracellular Ca(+2) to higher peak and steady-state levels. Env from R5 and X4 primary isolates evoked similar current responses as the corresponding prototype strains. Thus, the interaction of HIV-1 gp120 with CCR5 or CXCR4 evokes complex and distinct signaling responses in primary macrophages, and gp120-evoked signals differ from those activated by the coreceptors' chemokine ligands. Intracellular signaling responses of macrophages to HIV-1 may modulate postentry steps of infection and cell functions apart from infection.
Figures
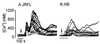
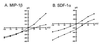
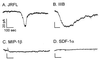
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

