Inactivation of photosystems I and II in response to osmotic stress in Synechococcus. Contribution of water channels
- PMID: 10759516
- PMCID: PMC58955
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.122.4.1201
Inactivation of photosystems I and II in response to osmotic stress in Synechococcus. Contribution of water channels
Abstract
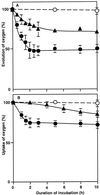
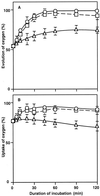
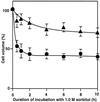
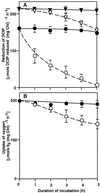
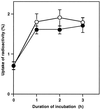
The effects of osmotic stress due to sorbitol on the photosynthetic machinery were investigated in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus R-2. Incubation of cells in 1.0 M sorbitol inactivated photosystems I and II and decreased the intracellular solute space by 50%. These effects of sorbitol were reversible: Photosynthetic activity and cytoplasmic volume returned to the original values after removal of the osmotic stress. A blocker of water channels prevented the osmotic-stress-induced inactivation and shrinkage of the intracellular space. It also prevented the recovery of photosynthetic activity and cytoplasmic volume when applied just before release from osmotic stress. Inhibition of protein synthesis by lincomycin had no significant effects on the inactivation and recovery processes, an observation that suggests that protein synthesis was not involved in these processes. Our results suggest that osmotic stress decreased the amount of water in the cytoplasm via the efflux of water through water channels (aquaporins), with resultant increases in intracellular concentrations of ions and a decrease in photosynthetic activity.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson JM, Andersson B. The dynamic photosynthetic membrane and regulation of solar energy conversion. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988;13:352–355. - PubMed
-
- Arnon DI, McSwain BD, Tsujimoto HY, Wada K. Photochemical activity and components of membrane preparations from blue-green algae: I. Coexistence of two photosystems in relation to chlorophyll a and removal of phycocyanin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974;357:231–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

