Down-regulation of the T cell receptor CD3 zeta chain in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and its influence on T cell responsiveness
- PMID: 10759780
- PMCID: PMC1905626
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01180.x
Down-regulation of the T cell receptor CD3 zeta chain in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and its influence on T cell responsiveness
Abstract
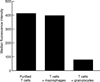
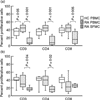
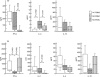
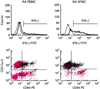
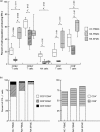
T cells implicated in chronic inflammatory diseases such as RA respond weakly when stimulated in vitro with mitogen or antigen. The mechanism behind this hyporesponsiveness is unclear, but a depressed expression of the T cell receptor (TCR)-associated CD3zeta chain has been suggested. In the present work we describe a low expression of CD3zeta in synovial fluid (SF) T cells from RA patients compared with peripheral blood (PB) T cells, but no difference in CD3zeta expression between RA and healthy control PB T cells. In vitro studies demonstrated that granulocytes but not SF macrophages are able to down-regulate the expression of CD3zeta. Through stimulation with anti-CD3 antibodies we demonstrated that the TCR-dependent proliferative response was decreased in SF T cells compared with PB T cells. Stimulation with phorbol ester and ionomycin also resulted in a low proliferative response of SF T cells, indicating that both signal transduction through the TCR (stimulation with anti-CD3) and events further downstream in the signalling pathways (stimulation with phorbol ester and ionomycin) are affected. A similar depression of T cell activity was observed when induction of IL-2 and IL-4 was measured. However, SF T cells were not defective in the induction of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) when stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)/ionomycin, in contrast to the diminished IFN-gamma response observed after stimulation with anti-CD3. This indicates that the hyporesponsiveness of SF T cells can not be generalized to all T cell functions. The differential response to external stimuli is likely to be of importance for the capacity of SF T cells to influence inflammatory reactions.
Figures
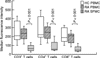
References
-
- Kiessling R, Kono K, Petersson M, et al. Immunosuppression in human tumor–host interaction. Role of cytokines and alterations in signal-transducing molecules. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1996;18:227–42. - PubMed
-
- Finke JH, Zea AH, Stanley J, et al. Loss of T-cell receptor zeta chain and p56lck in T-cells infiltrating human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1993;53:5613–6. - PubMed
-
- Nakagomi H, Petersson M, Magnusson I, et al. Decreased expression of the signal-transducing zeta chains in tumor-infiltrating T-cells and NK cells of patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1993;53:5610–2. - PubMed
-
- Zea AH, Curti BD, Longo DL, et al. Alterations in T cell receptor and signal transduction molecules in melanoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1:1327–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

