Increased synovial fluid levels of soluble CD23 are associated with an erosive status in rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- PMID: 10759783
- PMCID: PMC1905611
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01198.x
Increased synovial fluid levels of soluble CD23 are associated with an erosive status in rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Abstract
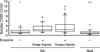
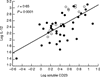
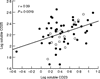
Synovial fluid (SF) levels of soluble CD23 (sCD23) were determined in 96 patients presenting with an inflammatory knee effusion (73 with RA and 23 with reactive arthritis (ReA) serving as a control inflammatory non-erosive group) and were correlated with the degree of joint destruction, with local immune parameters (IL-1beta, IL-3, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12 and sCD25) and with serum markers of inflammation, C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. RA patients, classified as erosive or not according to Larsen's grade, were separated as follows: (i) 13 patients with non-erosive RA; (ii) 16 RA patients with erosions in hands but not in knees, matched for disease duration with the first group; (iii) 44 RA patients with hand and knee erosions, matched with the second group for rheumatoid factor positivity but of longer disease duration. SF sCD23 levels were significantly increased in both erosive RA groups compared with non-erosive diseases, whether RA or ReA (P < 0.05), whose SF levels were not different. SF IL-10 showed a similar profile to that of SF sCD23 and was the only other parameter characteristic of erosive RA, but no direct correlation was found between the two. SF sCD23 was significantly correlated with IL-12 (r = 0.65, P = 0.0001) and sCD25 (r = 0.39, P = 0.0019) exclusively in the two erosive RA populations. In conclusion, these data showing that increased levels of sCD23 are not only found in the SF of erosive joints but also in knee SF of patients with erosive RA but without knee x-ray-diagnosed erosions suggest that this parameter might be of predictive value for joint destruction. Longitudinal studies are however needed to confirm its potential clinical interest.
Figures
References
-
- Delespesse G, Suter U, Mossalayi D, et al. Expression, structure and function of the CD23 antigen. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:149–91. - PubMed
-
- Delespesse G, Sarfati M, Wu CY, Fournier S, Letellier M. The low-affinity receptor for IgE. Immunol Rev. 1992;125:77–97. - PubMed
-
- Sarfati M, Fournier S, Wu CY, Delespesse G. Expression, regulation and function of human Fc epsilon RII (CD23) antigen. Immunol Res. 1992;11:260–72. - PubMed
-
- Liu YJ, Cairns JA, Holder MJ, Abbot SD, Jansen KU, Bonnefoy JY, Gordon J, MacLennan ICM. Recombinant 25-kDa CD23 and interleukin 1α promote the survival of germinal center B cells: evidence for bifurcation in the development of centrocytes rescued from apoptosis. Eur J Immunol. 1991;21:1107–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

