Efficient targeted mutagenesis in Borrelia burgdorferi
- PMID: 10762244
- PMCID: PMC111306
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.9.2445-2452.2000
Efficient targeted mutagenesis in Borrelia burgdorferi
Abstract
Genetic studies in Borrelia burgdorferi have been hindered by the lack of a nonborrelial selectable marker. Currently, the only selectable marker is gyrB(r), a mutated form of the chromosomal gyrB gene that encodes the B subunit of DNA gyrase and confers resistance to the antibiotic coumermycin A(1). The utility of the coumermycin-resistant gyrB(r) gene for targeted gene disruption is limited by a high frequency of recombination with the endogenous gyrB gene. A kanamycin resistance gene (kan) was introduced into B. burgdorferi, and its use as a selectable marker was explored in an effort to improve the genetic manipulation of this pathogen. B. burgdorferi transformants with the kan gene expressed from its native promoter were susceptible to kanamycin. In striking contrast, transformants with the kan gene expressed from either the B. burgdorferi flaB or flgB promoter were resistant to high levels of kanamycin. The kanamycin resistance marker allows efficient direct selection of mutants in B. burgdorferi and hence is a significant improvement in the ability to construct isogenic mutant strains in this pathogen.
Figures
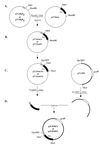
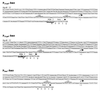
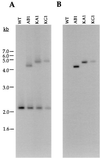
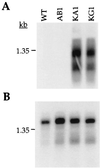
References
-
- Bono J L, Tilly K, Stevenson B, Hogan D, Rosa P. Oligopeptide permease in Borrelia burgdorferi: putative peptide-binding components encoded by both chromosomal and plasmid loci. Microbiology. 1998;144:1033–1044. - PubMed
-
- Burgdorfer W, Barbour A G, Hayes S F, Benach J L, Grunwaldt E, Davis J P. Lyme disease—a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982;216:1317–1319. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

