Evidence for Na(+) influx via the NtpJ protein of the KtrII K(+) uptake system in Enterococcus hirae
- PMID: 10762252
- PMCID: PMC111314
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.9.2507-2512.2000
Evidence for Na(+) influx via the NtpJ protein of the KtrII K(+) uptake system in Enterococcus hirae
Abstract
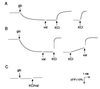
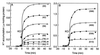
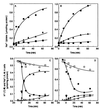
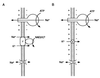
The ntpJ gene, a cistron located at the tail end of the vacuolar-type Na(+)-ATPase (ntp) operon of Enterococcus hirae, encodes a transporter of the KtrII K(+) uptake system. We found that K(+) accumulation in the ntpJ-disrupted mutant JEM2 was markedly enhanced by addition of valinomycin at pH 10. Studies of the membrane potential (DeltaPsi; inside negative) by 3, 3'-dihexyloxacarbocyanine iodide fluorescence revealed that the DeltaPsi was hyperpolarized at pH 10 in JEM2; the DeltaPsi values of the parent strain ATCC 9790 and JEM2, estimated by determining the equilibrium distribution of K(+) or Rb(+) in the presence of valinomycin, were -118 and -160 mV, respectively. DeltaPsi generation at pH 10 was accomplished by an electrogenic Na(+) efflux via the Na(+)-ATPase, whose levels in the two strains were quite similar. Na(+) uptake driven by an artificially imposed DeltaPsi (inside negative) was missing in JEM2, suggesting that NtpJ mediates Na(+) movement in addition to K(+) movement. Finally, the growth of JEM2 arrested in K(+)-limited high-Na(+) medium at pH 10 was restored by addition of valinomycin. These results suggest that NtpJ mediates electrogenic transport of K(+) as well as Na(+), that it likely mediates K(+) and Na(+) cotransport, and that Na(+) movement via NtpJ is the major Na(+) reentry pathway at high pH values.
Figures



References
-
- Abrams A. The proton-translocating membrane ATPase (F1Fo) in Streptococcus faecalis. In: Martonosi A N, editor. Enzymes in biological membranes. 2nd ed. Vol. 4. New York, N.Y: Plenum Press; 1985. pp. 177–193.
-
- Bakker E P. Accumulation of thallous ions (Tl+) as a measure of the electrical potential difference across the cytoplasmic membrane of bacteria. Biochemistry. 1978;17:2899–2904. - PubMed
-
- Bakker, E. P., and F. M. Harold. 1980. Energy coupling to potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis: interplay of ATP and the protonmotive force. 255:433–440. - PubMed
-
- Diatloff E, Kumar R, Schachtman D P. Site directed mutagenesis reduces the Na+ affinity of HKT1, an Na+ energized high affinity K+ transporter. FEBS Lett. 1998;432:31–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

