Antiviral effect of nitric oxide during Japanese encephalitis virus infection
- PMID: 10762444
- PMCID: PMC2517721
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2613.2000.00148.x
Antiviral effect of nitric oxide during Japanese encephalitis virus infection
Abstract
The ability of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) and JEV-induced macrophage derived neutrophil chemotactic factor (MDF) to produce nitric oxide (NO), and the possible antiviral effect of NO during JEV infection, was investigated. Splenic macrophages of JEV infected mice produced maximum NO in vivo at day 7 post infection, and in vitro at 24 h after JEV stimulation. MDF-induced NO production was dose dependent and maximal at 60 min after MDF treatment. The response was sensitive to anti-MDF antibody treatment and the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA). Pretreatment of mice with L-NMMA increased the mortality to 100% in JEV infected mice in vivo and inhibited NO production in vitro, while MDF stimulated macrophages inhibited virus replication with high levels of NO production. MDF treatment increased the survival rate of JEV infected mice. The findings thus demonstrate that MDF induces production of NO during JEV infection, which has an antiviral effect. This may be one of the important mechanisms of natural immunity in controlling the initial stages of JEV infection.
Figures
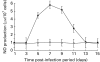




 ) macrophages after 24 h of in vitro JEV stimulation, as described in Materials and methods. Controls consisted of cells treated with MDF alone (
) macrophages after 24 h of in vitro JEV stimulation, as described in Materials and methods. Controls consisted of cells treated with MDF alone ( ) or unstimulated (□). Values are presented as A.M. ± SD of six cultures.
) or unstimulated (□). Values are presented as A.M. ± SD of six cultures.
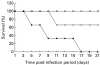
 ). As control (□) mock infected mice were also treated with MDF. The survival rate of the mice was monitored daily for three weeks.
). As control (□) mock infected mice were also treated with MDF. The survival rate of the mice was monitored daily for three weeks.References
-
- Chen L-K, Liao C-L, Lin C-G, et al. Persistence of Japanese encephalitis virus is assosiated with abnormal expression of the nonstructural protein NS1 in host cell. Virology. 1996;217:220–229. - PubMed
-
- Corriveau CC, Madara PJ, Van Dervort AL, Tropea MM, Wesley RA, Danner RL. Effect of nitric oxide on chemotaxis and endotoxin-induced interleukin-8 production in human neutrophils. J. Infect. Dis. 1998;177:116–126. - PubMed
-
- Ding AH, Nathan CF, Stuehr DJ. Release of reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J. Immunol. 1988;141:2407–2412. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

