Cell cycle. A new check on issuing the licence
- PMID: 10766226
- PMCID: PMC3605502
- DOI: 10.1038/35007187
Cell cycle. A new check on issuing the licence
Figures
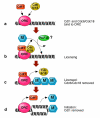
Comment on
-
XCDT1 is required for the assembly of pre-replicative complexes in Xenopus laevis.Nature. 2000 Apr 6;404(6778):622-5. doi: 10.1038/35007104. Nature. 2000. PMID: 10766247
-
The Cdt1 protein is required to license DNA for replication in fission yeast.Nature. 2000 Apr 6;404(6778):625-8. doi: 10.1038/35007110. Nature. 2000. PMID: 10766248
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

